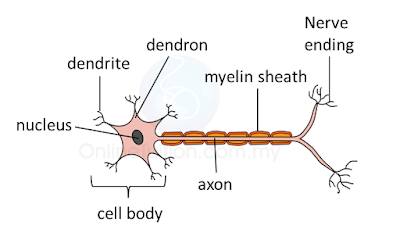
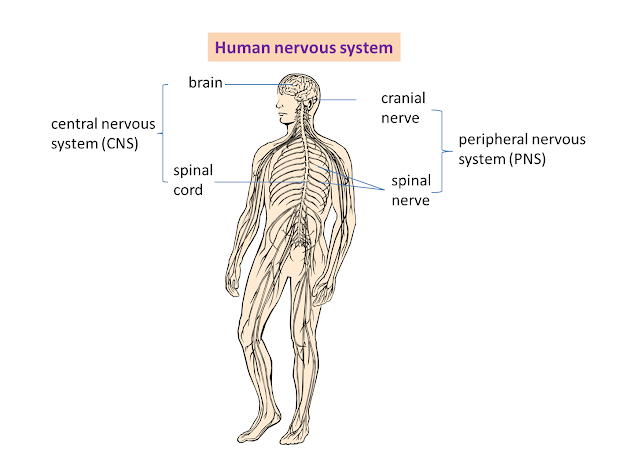
- The basic unit of the nervous system is neurone.
- The function of neurone is to carry impulses.
- Each part of s neurone plays an important role in the transmission of nervous impulses.
Neurone Part |
Function |
Cell body |
Controls all activities of the neurone |
Dendron |
Transmits impulses towards a cell body |
Dendrite |
Receives impulse from other neurone and transmits them to cell body |
Axon |
Transmits impulses out of cell body |
Myelin sheath |
Speed up the transmission of impulses. Insulator that prevents the leakage of impulses. |