Soalan 4:
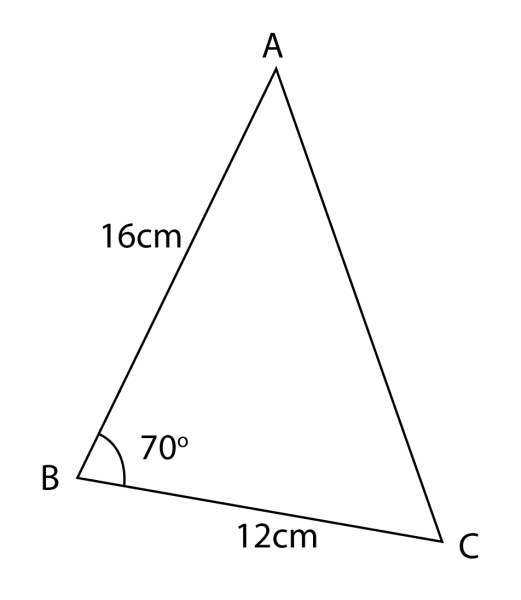
Dalam rajah di bawah, ABC ialah sebuah segi tiga. AGJB, AHC dan BKC ialah garis lurus. Garis lurus JK adalah berserenjang kepada BC.
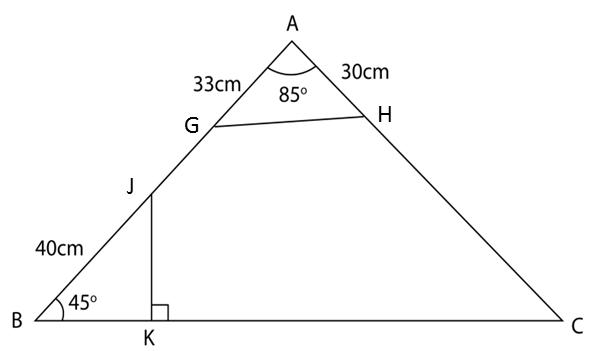
Diberi bahawa BG = 40cm, GA = 33 cm, AH = 30 cm, GAH = 85o dan JBK = 45o.
(a) Hitung panjang, dalam cm, bagi
i. GH
ii. HC
(b) Luas segi tiga GAH adalah dua kali luas segi tiga JBK. Hitung panjang, dalam cm, bagi BK.
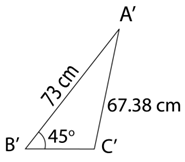
(c) Lakar segi tiga A’B’C’ yang mempunyai bentuk yang berlainan daripada segi tiga ABC dengan keadaan A’B’ = AB, A’C’ = AC dan ∠ A’B’C’ = ∠ ABC.
Penyelesaian:
(a)(i)
Guna petua kosinus,
GH2 = AG2 + AH2 – 2 (AG)(AH) kos ∠ GAH
GH2 = 332+ 302 – 2 (33)(30) kos 85o
GH2 = 1089 + 900 – 172.57
GH2 = 1816.43
GH = 42.62 cm
(a)(ii)
∠ ACD = 180o – 45o – 85o = 50o
Guna petua sinus,
ACsin45∘=73sin50∘AC=73×sin45∘sin50∘
AC = 67.38 cm
Oleh itu, HC = 67.38 – 30 = 37.38 cm
(b)
Area of ∆ GAH = ½ (33)(30) sin 85o = 493.12 cm2
Katakan panjang BK = JK = x
2 × Area of ∆ JBK = Area of ∆ GAH
2 × [½ (x)(x)] = 493.12
x2 = 493.12
x = 22.21 cm
BK = 22.21 cm
BK = 22.21 cm
(c)