6.1 Pythagoras’ Theorem
6.1.1 Pythagoras’ Theorem
1. In a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle.
2. Pythagoras’ Theorem:
|
In a right-angled triangle, the square
of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum
of the squares of the other two sides.
|
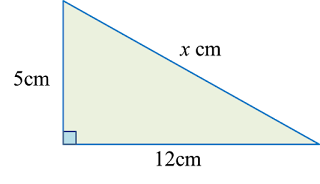
Example 1:
Solution:
x2=52+122=25+144x=√169=13
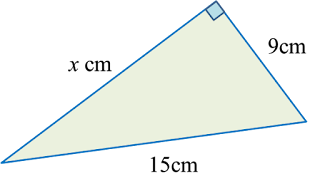
Example 2:
Solution:
x2=152−92=225−81x=√144=12
3. Pythagorean triples are three whole numbers that form the sides of a right-angled triangle.
Example:
(a) 3, 4, 5
(b) 6, 8, 10
(b) 6, 8, 10
(c) 5, 12, 13
(d) 8, 15, 17
(d) 8, 15, 17
(e) 9, 12, 15
6.1.2 The Converse of the Pythagoras’ Theorem
|
In a triangle, if the sum of the squares of the two sides
is equal to the square of the longest side, then the angle
opposite the longest side is a right angle.
|