3 Types of Radioactive Emission
Alpha Particle

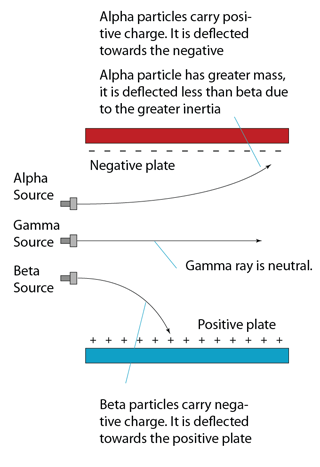
- carries positive charge.
- most strongly ionizing of the nuclear radiations.
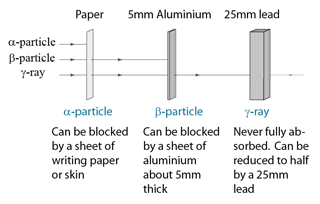
- least penetrating. Range in air is only a few centimetres, and can be stopped by a thick sheet of paper.
Beta Particle

- carry a negative charge.
- much less ionizing than alpha emission.
- more penetrating than alpha emission..
- have a range of a metre or so in air,
- can be stopped by a few millimetres of Perspex or aluminium.
Gamma Radiation

- often emitted at the same time as an alpha or beta particle.
- least ionizing of the nuclear radiations,
- most penetrating.
- their intensity is greatly reduced by several centimetres of lead, but they are never completely absorbed.
Ionising Effect
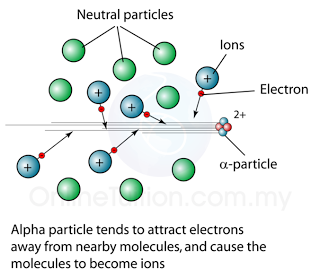
- All alpha, beta and gamma emission can cause ionising effect.
- Alpha particle has high ionizing power.Beta particle has low ionizing power.
- Gamma ray has very low ionizing power.
Penetrating Power
Deflection in Electric Field
Deflection in Magnetic Field
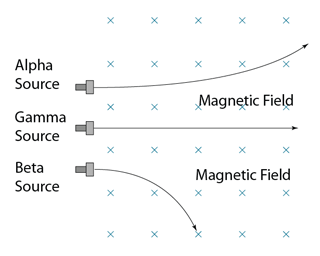
- Alpha and beta emission can be deflected by a magnetic field.
- The direction of deflection can be determined by using Fleming’s Left Hand Rule.
- Beta particle deflected more compare to alpha particle due to its much smaller mass.
Summary
| Characteristic |
Alpha Particle
|
Beta Particle
|
Gamma Ray
|
| Symbol |
α
|
β
|
γ |
| Nature |
Nucleus of Helium
|
High speed electron | Electromagnetic wave |
| Charge |
+2
|
-1
|
Neutral
|
| Ionizing Effect |
strong
|
weak
|
Very weak
|
| Absorted by | Sheet of writing paper |
About 5mm of aluminium
|
Never fully absorded. 25mm of lead reduces intensity to half
|
| Deflection in Electric Field |
Can be deflected
|
Can be deflected
|
Not deflected
|
| Deflection in magnetic Field |
Can be deflected
|
Can be deflected
|
Not deflected
|
| Speed |
Up to 10% of the speed of light
|
Up to 90% of the speed of light
|
Speed of light
|
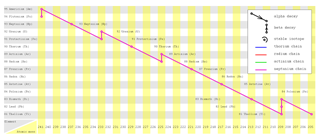
Series Decay
- Sometimes after a radioactive decay, the daughter nuclide formed is still unstable.
- It will further decay into another nuclide which may also unstable.
- This process continues until a stable nuclide is reached. This is called a series decay.
- Each decay will emit either an alpha particle or a beta particle and may be gamma ray.
- Figure below shows a series decay started from plutonium-241 to formed Thallium-205 eventually.
 |
| (This image is created by Johantheghost under creative common licence) |