Domain and Codomain
- In the relation between one set and another, the first set is known as the domain and the second set is known as the codomain.
- Elements in the domain is called objects, whereas elements in the codomain mapped to the objects is called the image.
- Elements in the codomain not mapped to the objects are not the image.
- All images in codomain can be written as a set known as range.
Example:
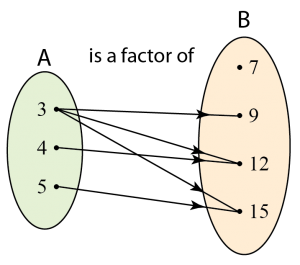
Domain = {3, 4, 5}
Codomain = {7, 9, 12, 15}
Range = {9, 12, 15} [Note: 7 is not an image because it is not mapped to any object.]
3 is the object of 9, 12 and 15.
4 is the object of 12.
5 is the object of 15.
9, 12 and 15 are the images of 3.
12 is the image of 4.
15 is the image of 5.

Domain = {3, 4, 5}
Codomain = {7, 9, 12, 15}
Range = {9, 12, 15} [Note: 7 is not an image because it is not mapped to any object.]
3 is the object of 9, 12 and 15.
4 is the object of 12.
5 is the object of 15.
9, 12 and 15 are the images of 3.
12 is the image of 4.
15 is the image of 5.