6.3 Areas of Polygons
(A) Area of Triangle
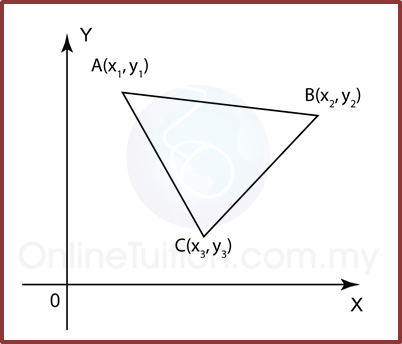
Area of Triangle
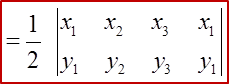
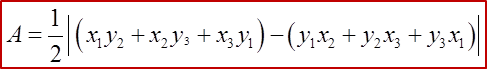
1. When the given points are taken in an anticlockwise direction the result is positive; taken in a clockwise direction the result is negative. The answer for the area must be given as a positive value.
Example 1:
Calculate the area of ∆ ABC with the vertices A (-5, 5), B (-2, -4),
C (4, -1).
Solution:
Area of △ ABC=12|−5 −2 4 5 −4 −1 −5 5|=12|(−5)(−4)+(−2)(−1)+(4)(5) −(5)(−2)−(−4)(4)−(−1)(−5)|=12|20+2+20+10+16−5|=12|63|=3112 unit2
(B) Area of Quadrilateral
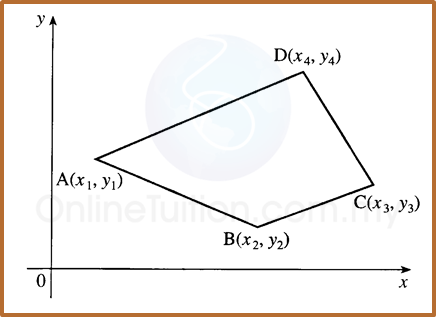
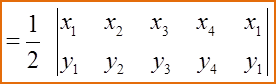
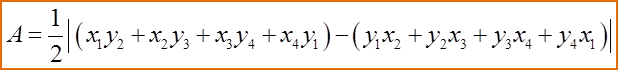

Area of Quadrilateral
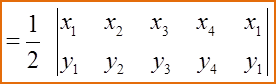
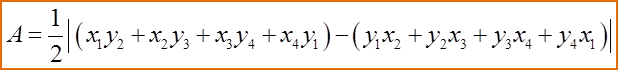
(C) If the points A, B and C are collinear, then the area of ∆ ABC is 0.
Example 2:
Find the values of k if the points P (2, 1), Q (6, k) and R (3k,
92
) are collinear.
Solution:
Area of △ PQR=012 |2 6 3k 1 k 92 21|=012|2k+27+3k−6−3k2−9|=0|−3k2+5k+12|=03k2−5k−12=0(3k+4)(k−3)=0 k=−43 or 3