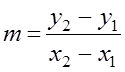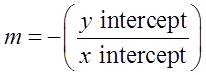6.4.1 Axes Intercepts and Gradient
(A) Formula for gradient:
2. Gradient of the line with knowing x–intercept and y–intercept is:
3. The gradient of the straight line joining P and Q is equal to the tangent of angle θ, where θ is the angle made by the straight line PQ and the positive direction of the x-axis.
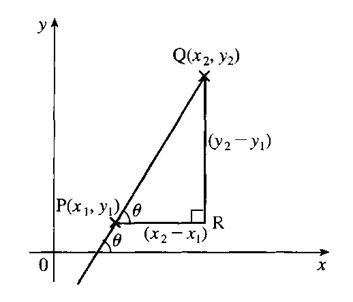
(B) Collinear points
The gradient of a straight line is always constant i.e.the gradient of AB is equal to the gradient of BC.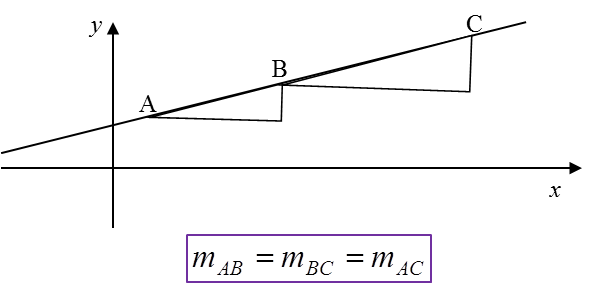
Example 1:
Example 2:
The gradient of the line passing through point (k, 1 – k) and point (–3k, –3) is 5. Find the value of k.
Solution:
Gradient, m=y2−y1x2−x1−3−(1−k)−3k−k=5−3−1+k−4k=5−4+k=−20k21k=4k=421
Solution:
Example 2:
Based on the diagram below, find the gradient of the line.
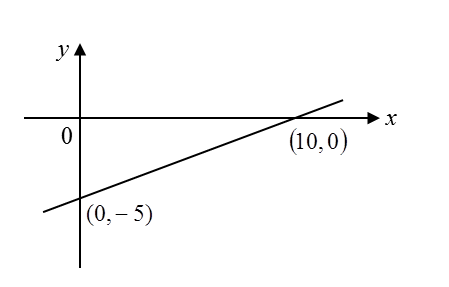

Solution:
Gradient, m=−(y interceptx intercept)=−(−510)=12