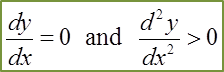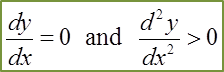(A) Second-Order Differentiation
The first derivative dydx=12x2−14x+5
1. When a function y = x3 + x2 – 3x + 6 is differentiated with respect to x, the derivative
dydx=3x2+2x−3
2. The second function
dydx
can be differentiated again with respect to x. This is called the second derivative of y with respect to x and can be written as
d2ydx2
.
3. Take note that
d2ydx2≠(dydx)2
.
For example,
If y = 4x3 – 7x2 + 5x – 1,
The first derivative dydx=12x2−14x+5
The second derivative
d2ydx2=24x−14
(B) Turning Points, Maximum and Minimum Points
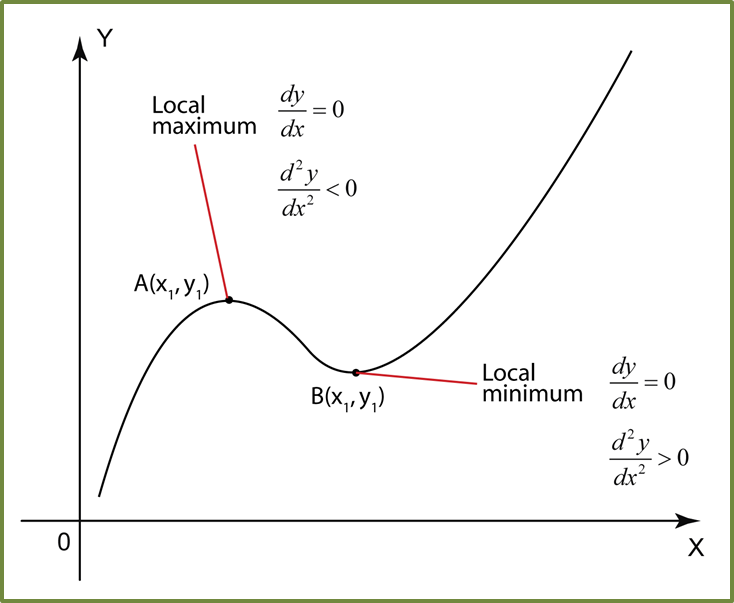

(a) At Turning Points A and B,
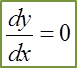
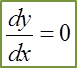
(b) At Maximum Point A,
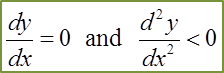
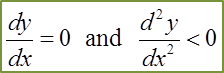
(c) At Minimum Point B,