Question 5:
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Using sine rule,sin∠ADC16.39=sin45∘14sin∠ADC=16.39×sin45∘14sin∠ADC=0.8278∠ADC=55.87∘ or (180∘−55.87∘)∠ADC=55.87∘ or 124.13∘
(c)(i)
Acute angle of ∠ADC=55.87∘∠CAD=180∘−45∘−55.87∘=79.13∘CDsin79.13∘=14sin45∘CD=14×sin79.13∘sin45∘=19.44 cm
(c)(ii)
Area of quadrilateral ABCD= Area of Δ ABC+Area of Δ ACD=12(16)(12)sin70∘+12(16.39)(14)sin79.13∘=90.21+112.67=202.88 cm2
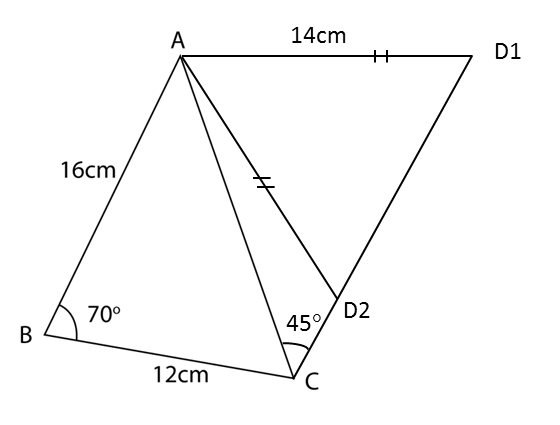
The diagram below shows a triangle ABC.
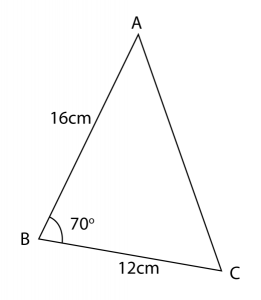

(a) Calculate the length, in cm, of AC.
(b) A quadrilateral ABCD is now formed so that AC is a diagonal, ∠ACD = 45° and AD = 14 cm. Calculate the two possible values of ∠ADC.
(c) By using the acute ∠ADC from (b), calculate
(i) the length, in cm, of CD,
(ii) the area, in cm2, of the quadrilateral ABCD
Solution:
(a)
Using cosine rule,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 – 2 (AB)(BC) ∠ABC
AC2 = 162 + 122 – 2 (16)(12) cos 70o
AC2 = 400 – 131.33
AC2 = 268.67
AC = 16.39 cm
(b)

Using sine rule,sin∠ADC16.39=sin45∘14sin∠ADC=16.39×sin45∘14sin∠ADC=0.8278∠ADC=55.87∘ or (180∘−55.87∘)∠ADC=55.87∘ or 124.13∘
(c)(i)
Acute angle of ∠ADC=55.87∘∠CAD=180∘−45∘−55.87∘=79.13∘CDsin79.13∘=14sin45∘CD=14×sin79.13∘sin45∘=19.44 cm
(c)(ii)
Area of quadrilateral ABCD= Area of Δ ABC+Area of Δ ACD=12(16)(12)sin70∘+12(16.39)(14)sin79.13∘=90.21+112.67=202.88 cm2