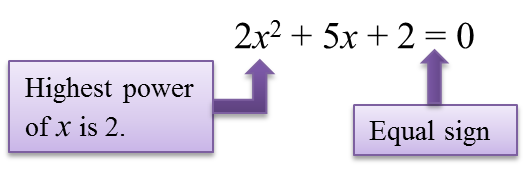
2.2 Factorisation of Quadratic Expression
(A) Factorisation quadratic expressions of the form ax2 + bx + c, b = 0 or c = 0
1. Factorisation of quadratic expressions is a process of finding two linear expressions whose product is the same as the quadratic expression.
2. Quadratic expressions ax2 + c and ax2 + bx that consist of two terms can be factorised by finding the common factors for both terms.
Example 1:
Factorise each of the following:
(a) 2x2+ 6
(b) 7p2– 3p
(c) 6x2– 9x
Solution:
(a) 2x2+ 6 = 2 (x2 + 3) ← (2 is common factor)
(b) 7p2– 3p = p (7p – 3) ← (p is common factor)
(c) 6x2– 9x = 3x (2x – 3) ← (3x is common factor)
(B) Factorisation of quadratic expressions in the form ax2 – c , where a and c are perfect squares
Example 2:
(a) 9p2– 16
(b) 25x2– 1
(c)
14−125x2
Solution:
(a) 9p2– 16 = (3p)2 – 42= (3p – 4) (3p + 4)
(b) 25x2– 1 = (5x)2 – 12= (5x – 1) (5x + 1)
(c)
14−125x2=(12)2−(15x)2=(12−15x)(12+15x)
(C) Factorisation quadratic expressions in the form ax2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0 and c ≠ 0
Example 3:
Factorise each of the following
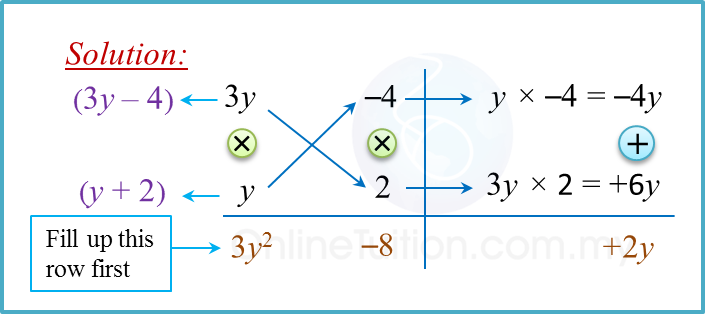
(a) 3y2+ 2y – 8
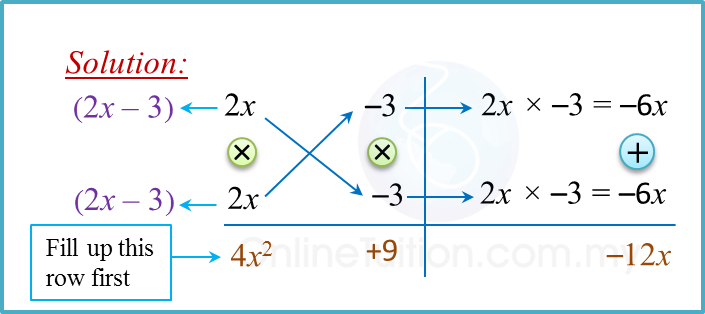
(b) 4x2– 12x + 9
Solution:
(a)
Factorise using the Cross Method
3y2+ 2y – 8 = (3y – 4) (y + 2)
(b)
4x2– 12x + 9 = (2x – 3) (2x – 3)