Question 1:
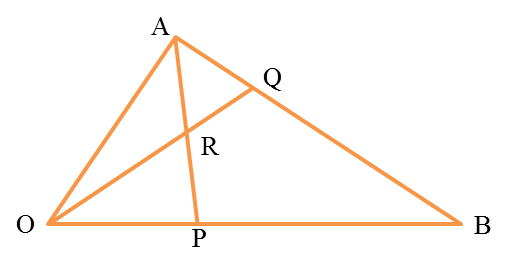
The above diagram shows triangle OAB. The straight line AP intersects the straight line OQ at R. It is given that OP=14OB, AQ=14AB, →OP=4b˜ and →OA=8a˜.
(a) Express in terms of a˜ and/ or b˜:
(i)→AP(ii)→OQ
(b)(i) Given that →AR=h→AP , state →AR in terms of h, a˜ and b˜.
(ii) Given that →RQ=k→OQ, state in terms of k, a˜ and b˜.
(c) Using →AQ=→AR+→RQ, find the value of h and of k.
Solution:
(a)(i)
→AP=→AO+→OP→AP=−→OA+→OP→AP=−8a˜+4b˜
(a)(ii)
→OQ=→OA+→AQ→OQ=8a˜+14→AB→OQ=8a˜+14(→AO+→OB)→OQ=8a˜+14(−8a˜+4→OP)→OQ=8a˜+14(−8a˜+4(4b˜))→OQ=8a˜−2a˜+4b˜→OQ=6a˜+4b˜
(b)(i)
→AR=h→AP→AR=h(−8a˜+4b˜)→AR=−8ha˜+4hb˜
(b)(ii)
→RQ=k→OQ→RQ=k(6a˜+4b˜)→RQ=6ka˜+4kb˜
(c)
→AQ=→AR+→RQ→AQ=−8ha˜+4hb˜+(6ka˜+4kb˜)→AO+→OQ=−8ha˜+4hb˜+6ka˜+4kb˜−8a˜+6a˜+4b˜=−8ha˜+6ka˜+4hb˜+4kb˜−2a˜+4b˜=−8ha˜+6ka˜+4hb˜+4kb˜−2=−8h+6k−1=−4h+3k→(1)4=4h+4k1=h+kk=1−h→(2)Substitute (2) into (1),−1=−4h+3(1−h)−1=−4h+3−3h−4=−7hh=47From (2),k=1−47=37
The above diagram shows triangle OAB. The straight line AP intersects the straight line OQ at R. It is given that OP=14OB, AQ=14AB, →OP=4b˜ and →OA=8a˜.
(a) Express in terms of a˜ and/ or b˜:
(i)→AP(ii)→OQ
(b)(i) Given that →AR=h→AP , state →AR in terms of h, a˜ and b˜.
(ii) Given that →RQ=k→OQ, state in terms of k, a˜ and b˜.
(c) Using →AQ=→AR+→RQ, find the value of h and of k.
Solution:
(a)(i)
→AP=→AO+→OP→AP=−→OA+→OP→AP=−8a˜+4b˜
(a)(ii)
→OQ=→OA+→AQ→OQ=8a˜+14→AB→OQ=8a˜+14(→AO+→OB)→OQ=8a˜+14(−8a˜+4→OP)→OQ=8a˜+14(−8a˜+4(4b˜))→OQ=8a˜−2a˜+4b˜→OQ=6a˜+4b˜
(b)(i)
→AR=h→AP→AR=h(−8a˜+4b˜)→AR=−8ha˜+4hb˜
(b)(ii)
→RQ=k→OQ→RQ=k(6a˜+4b˜)→RQ=6ka˜+4kb˜
(c)
→AQ=→AR+→RQ→AQ=−8ha˜+4hb˜+(6ka˜+4kb˜)→AO+→OQ=−8ha˜+4hb˜+6ka˜+4kb˜−8a˜+6a˜+4b˜=−8ha˜+6ka˜+4hb˜+4kb˜−2a˜+4b˜=−8ha˜+6ka˜+4hb˜+4kb˜−2=−8h+6k−1=−4h+3k→(1)4=4h+4k1=h+kk=1−h→(2)Substitute (2) into (1),−1=−4h+3(1−h)−1=−4h+3−3h−4=−7hh=47From (2),k=1−47=37