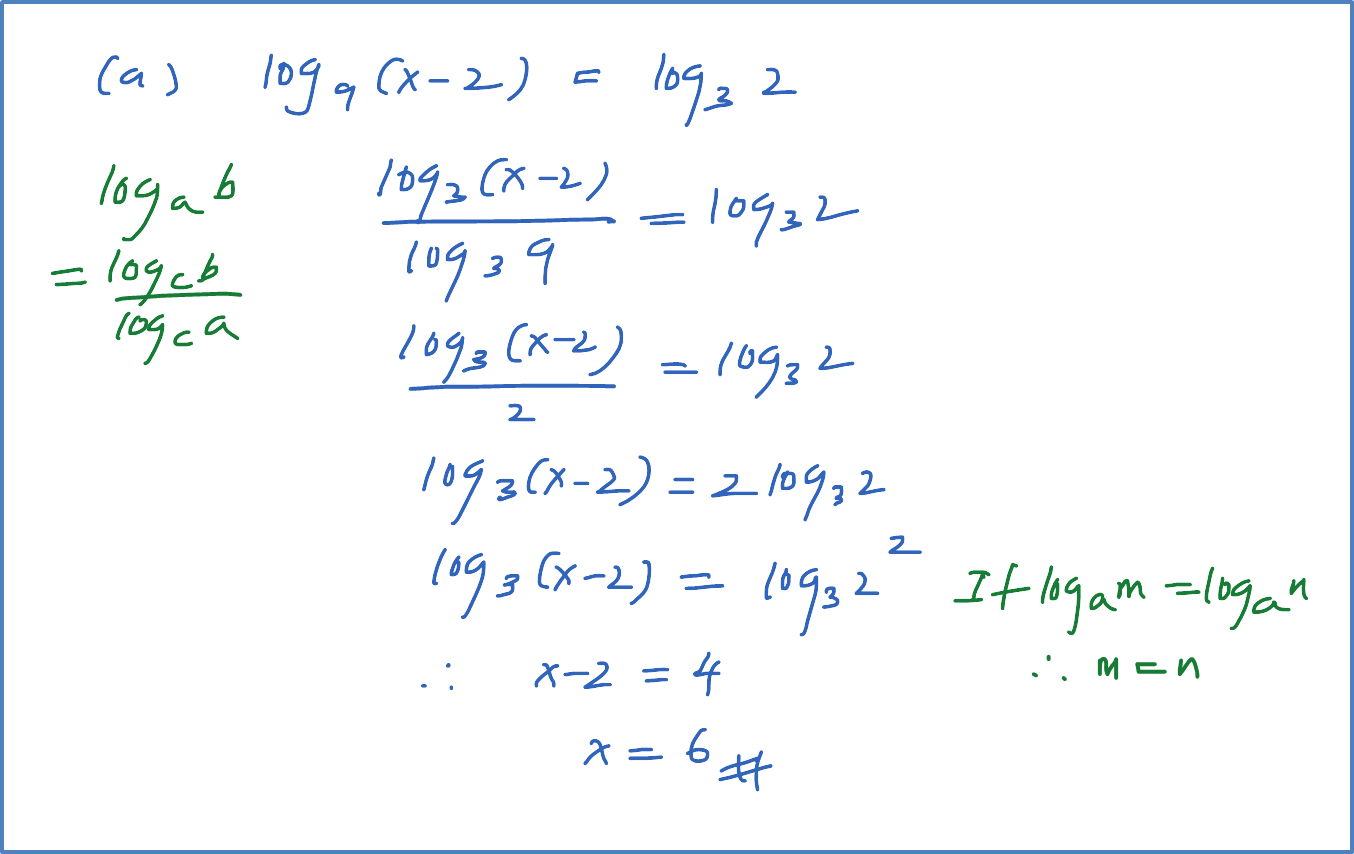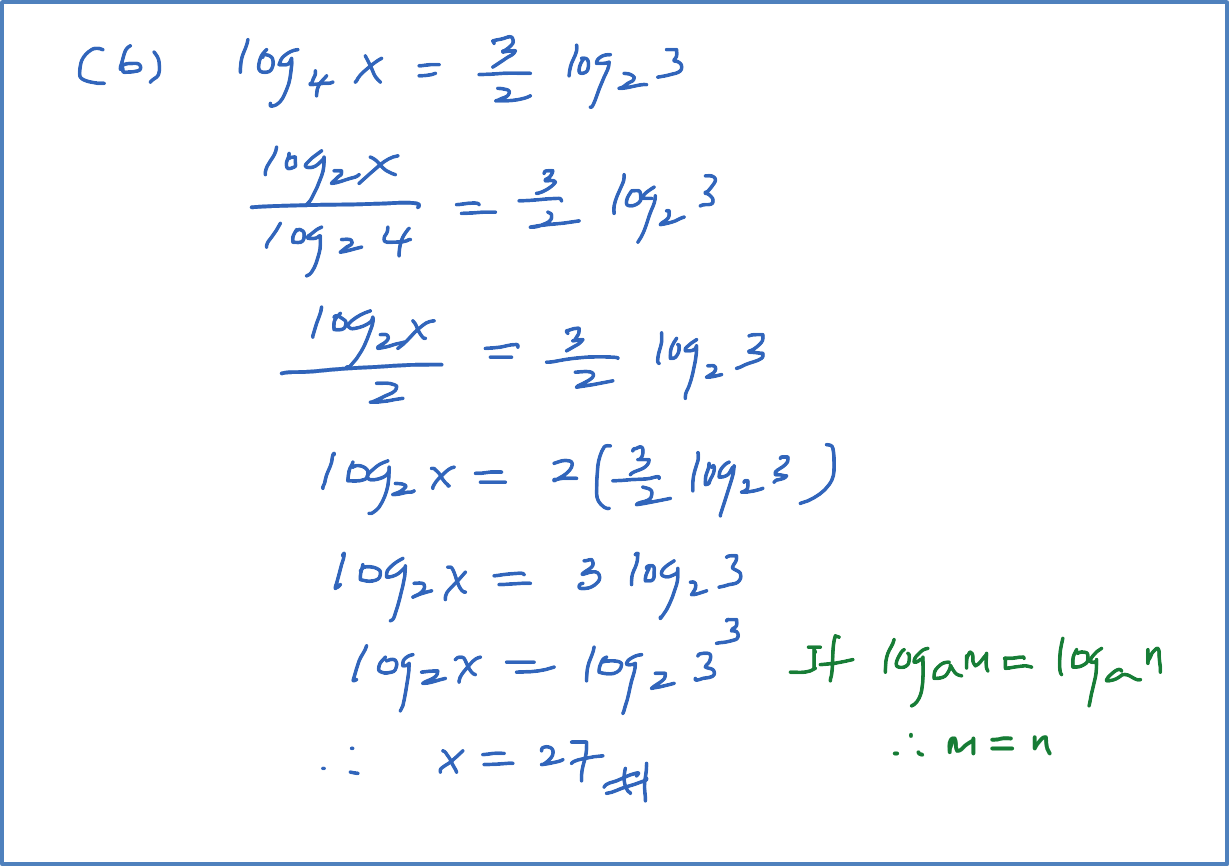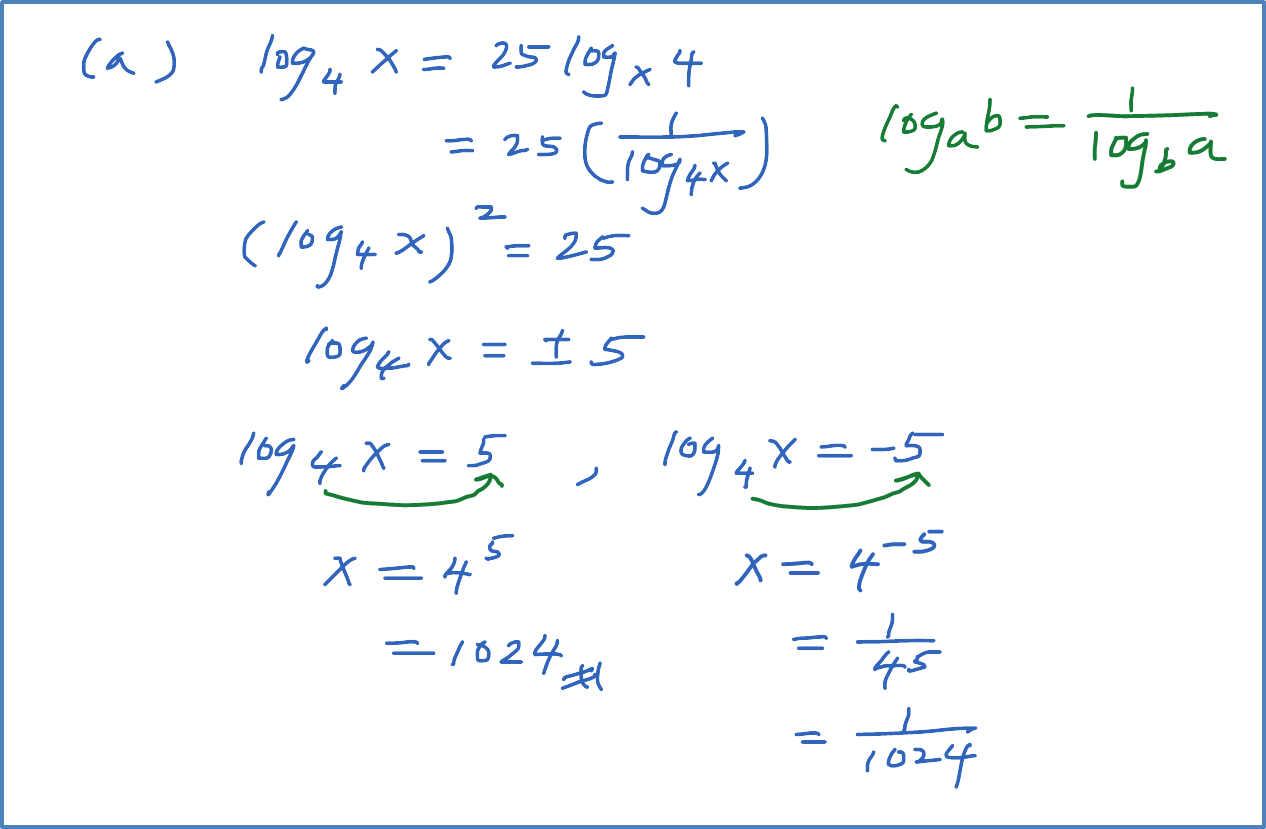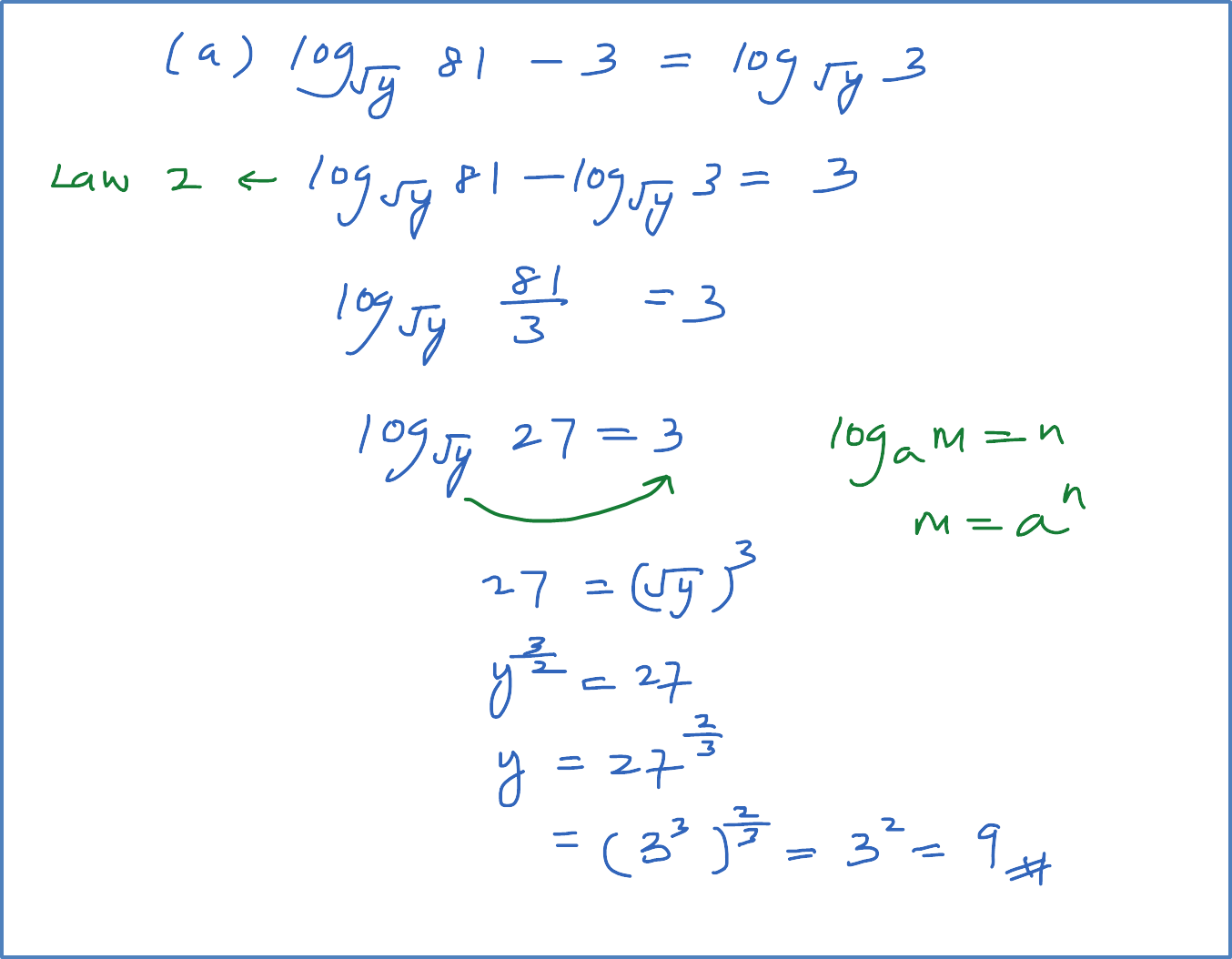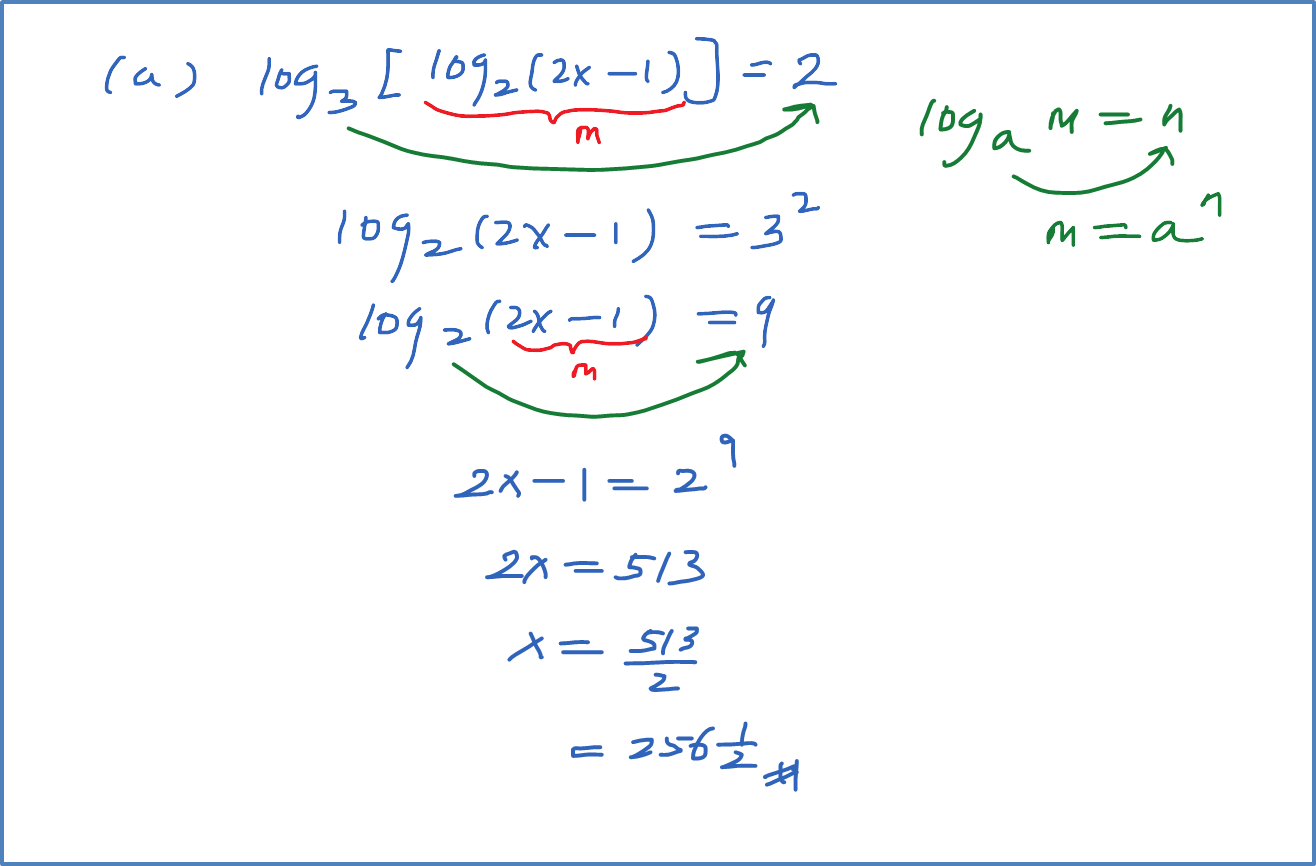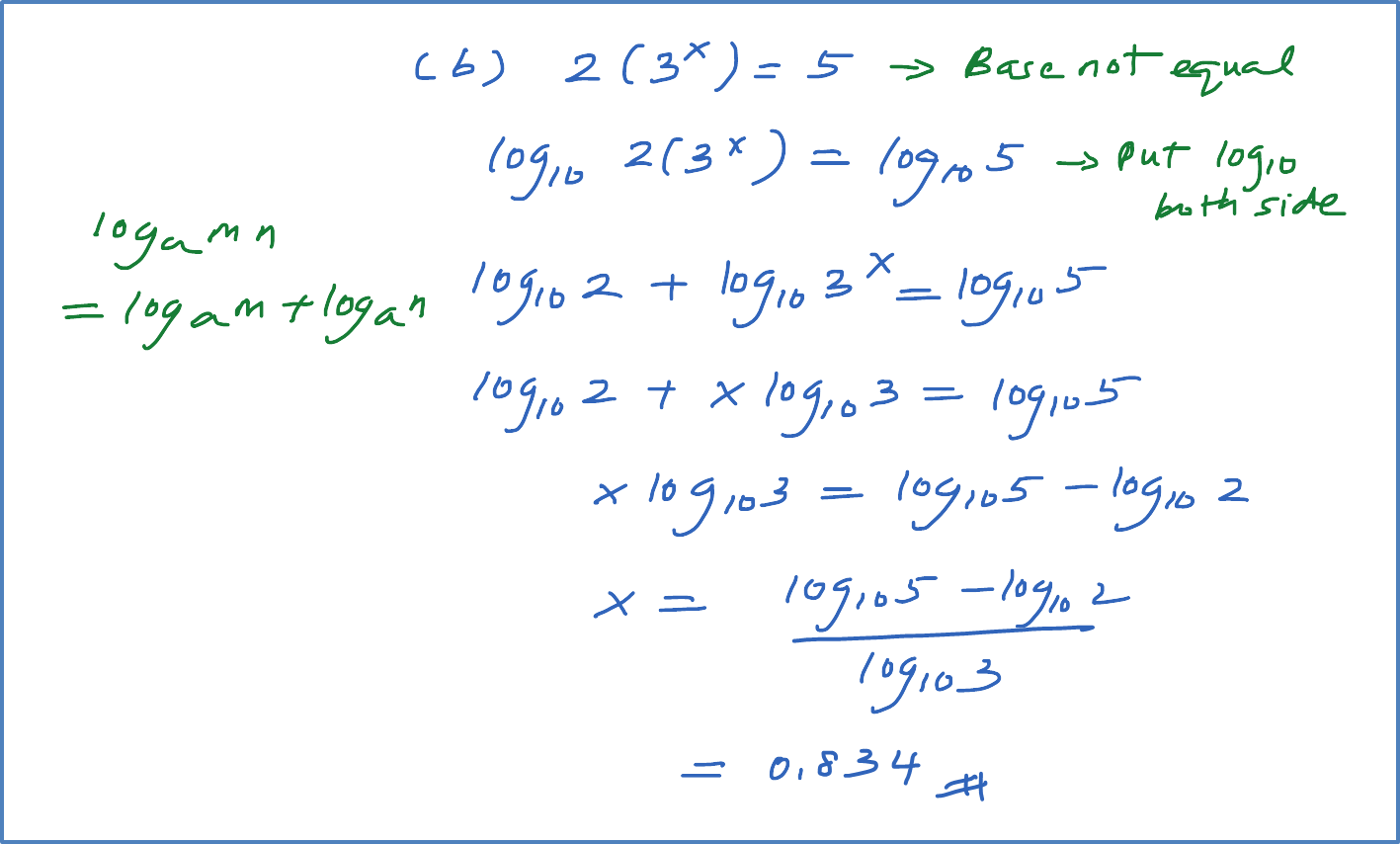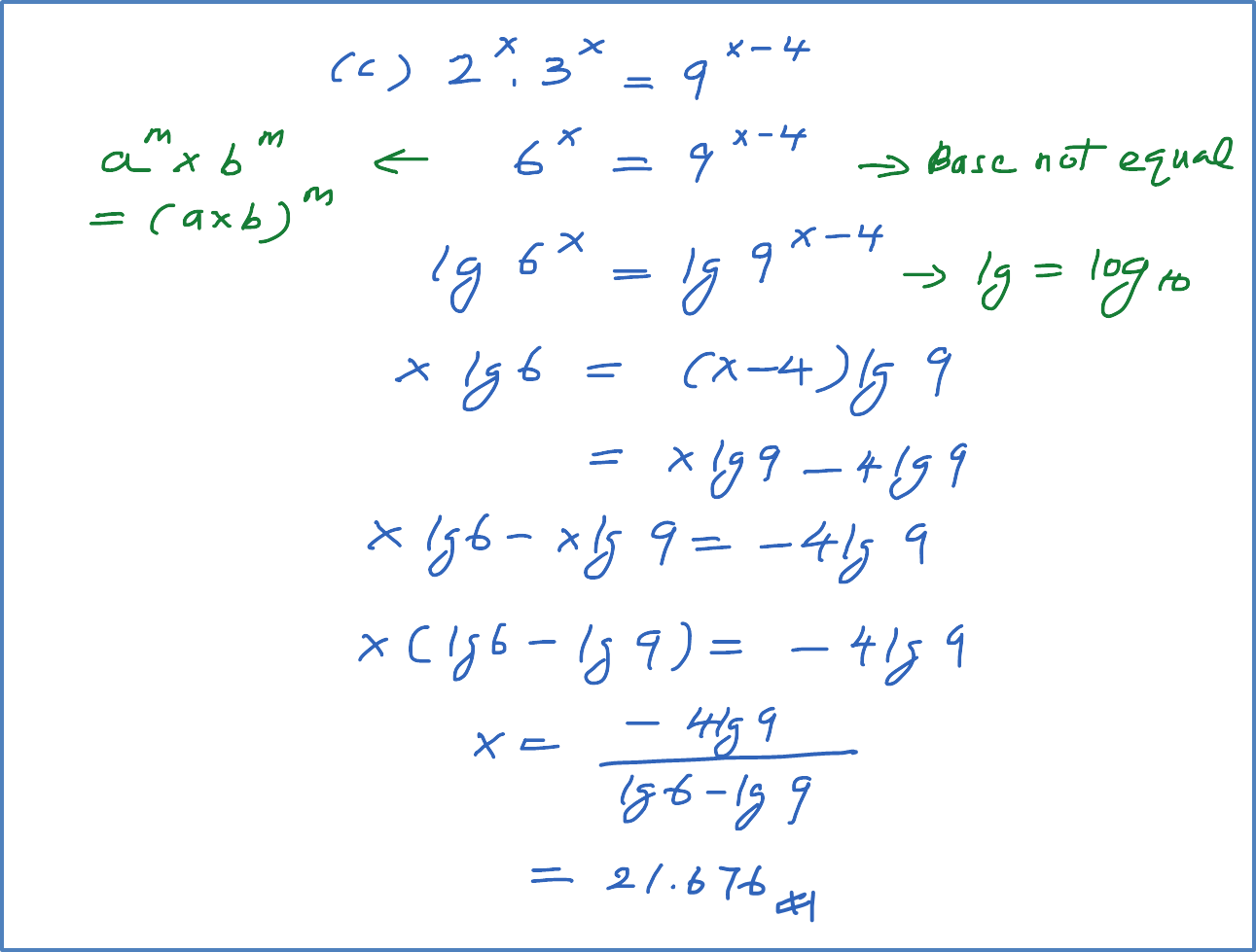5.6.1 Indices and Logarithms, SPM Practice (Long Questions)
Question 1:
(a) Find the value of
i. 2 log2 12 + 3 log25 – log2 15 – log2 150.
ii. log832
(b) Shows that 5n + 5n + 1 + 5n + 2 can be divided by 31 for all the values of n which are positive integer.
Solution:
(a)(i)
2 log2 12 + 3 log2 5 – log215 – log2 150
= log2 122 + log2 53– log2 15 – log2 150
=log2122×5315×150
= log2 8
= log2 23
= 3
(a)(ii)
log832=log232log28 =log225log223=53
(b)
5n + 5n + 1 + 5n + 2
= 5n + (5 × 5n ) + (52 × 5n )
= 5n (1 + 5 + 52)
= 31 × 5n
Therefore, 5n + 5n + 1 + 5n + 2 can be divided by 31 for all the values of n which are positive integer.
Question 2:
(a) Given log10 x = 3 and log10y = –2. Shows that 2xy – 10000y2 = 19.
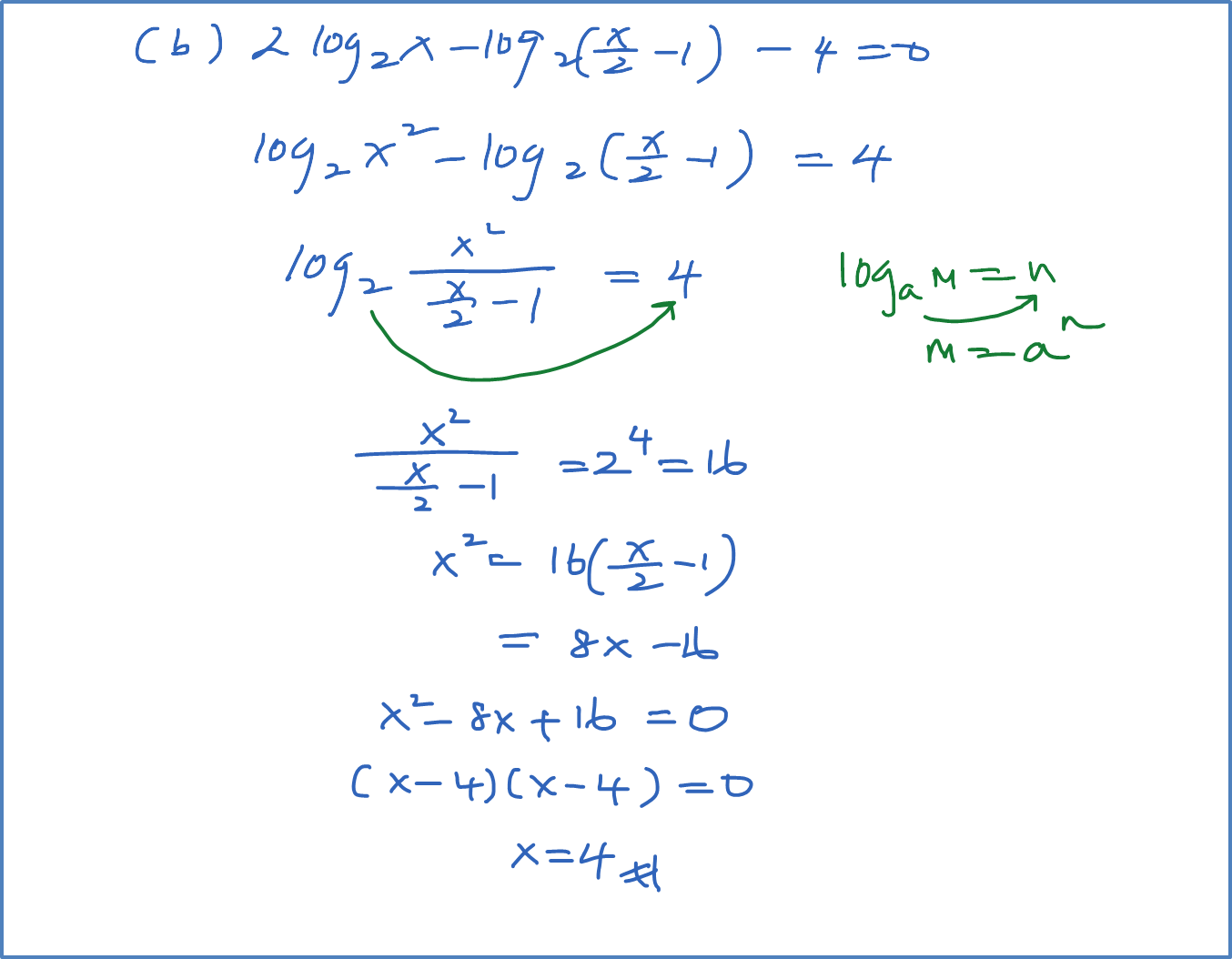
(b) Solve the equation log3 x = log9(x + 6).
Solution:
(a)
log10x = 3 → (x = 103)
log10y = –2 → (y = 10-2)
2xy – 10000y2 = 19
Left hand side:
2xy – 10000y2
= 2 × 103 × 10-2 – 10000 (10-2)2
= 20 – 10000 (10-4)
= 20 – 1
= 19
= right hand side
(b)
log3x=log9(x+6)log3x=log3(x+6)log39log3x=log3(x+6)log332log3x=log3(x+6)2
2log3 x= log3 (x + 6)
log3 x2= log3 (x + 6)
x2= x + 6
x2– x – 6 = 0
(x + 2) (x – 3) = 0
x = – 2 atau 3.
log3 (– 2) not accepted (logarithm of a negative number is undefined)
Jadi, x = 3.