8.2b Standard Normal Distribution Tables (Example 2)
Example 2:
Find the value of each of the following probabilities by reading the standard normal distribution tables.
(a) P (0.4 < Z < 1.2)
(b) P (–1 < Z < 2.5)
(c) P (–1.3 < Z < –0.5)
Solution:
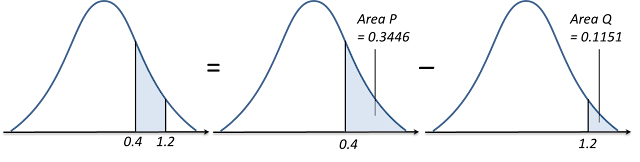
(a)
P (0.4 < Z < 1.2)
= Area P – Area Q
= Q (0.4) – Q (1.2) ← (reading from the standard normal distribution table for 0.4 and 1.2 are 0.3446 and 0.1151 respectively)
= 0.3446 – 0.1151
= 0.2295
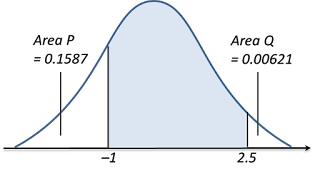
(b)
P (–1 < Z < 2.5)
= 1– Area P – Area Q
= 1 – Q (1) – Q (2.5)
= 1 – 0.1587 – 0.00621 ← (reading from the standard normal distribution table for 1 and 2.5 are 0.1587 and 0.00621 respectively)
= 0.8351
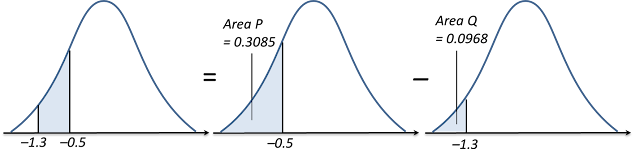
(c)
P (–1.3 < Z < –0.5)
= Area P – Area Q
= Q (0.5) – Q (1.3)
= 0.3085 – 0.0968 ← (reading from the standard normal distribution table for 0.5 and 1.3 are 0.3085 and 0.0968 respectively)