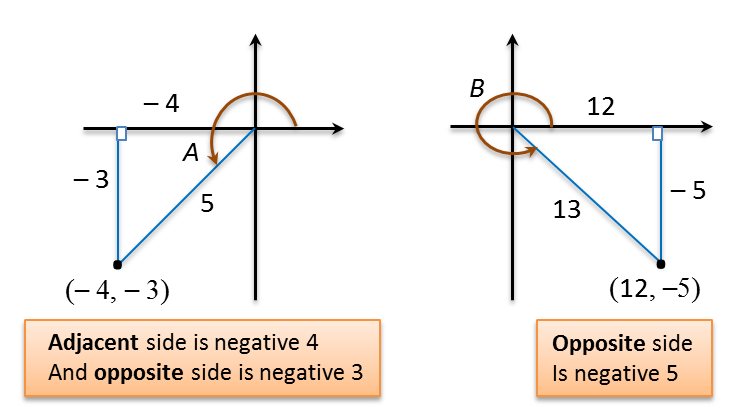
Example 3:
(a) Given that
sinP=35 and sinQ=513,
such that P is an acute angle and Q is an obtuse angle, without using tables or a calculator, find the value of cos (P + Q).
(b) Given that sinA=−35 and sinB=1213, such that A and B are angles in the third and fourth quadrants respectively, without using tables or a calculator, find the value of sin (A – B).
Solution:
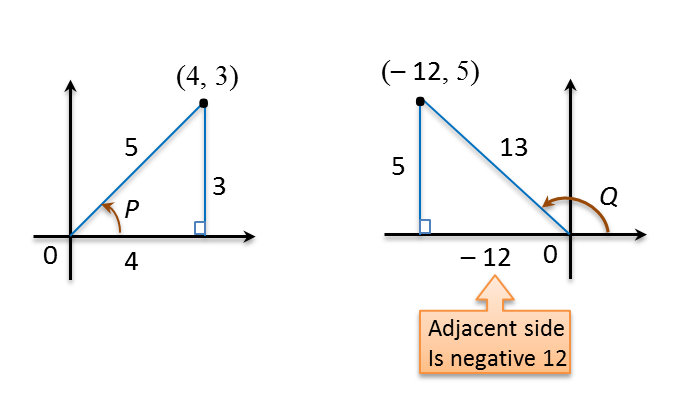 sinP=35,cosP=45sinQ=513,cosQ=−1213cos(P+Q)=cosAcosB−sinAsinB=(45)(−1213)−(35)(513)=−4865−1565=−6365
sinP=35,cosP=45sinQ=513,cosQ=−1213cos(P+Q)=cosAcosB−sinAsinB=(45)(−1213)−(35)(513)=−4865−1565=−6365
(b)