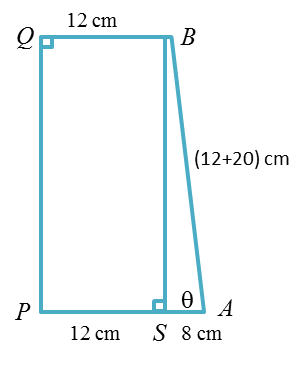
Question 3:
An arithmetic progression has 16 terms. The sum of the 16 terms is 188, and the sum of the even terms is 96. Find
(a) the first term and the common difference,
(b) the last term.
Solution:
(a) Let the first term = a
Common difference = d
Given the sum of the even terms = 96
(2) – (1):
16d – 15d = 24 – 23.5
d = 0.5
Substitute d = 0.5 into (2):
2a + 16 (0.5) = 24
2a + 8 = 24
2a = 16
a = 8
Therefore, first term = 8 and common difference = 0.5.
(b) Last term
= T2
= 8 + 15 (0.5)
= 8 +7.5
= 15.5
An arithmetic progression has 16 terms. The sum of the 16 terms is 188, and the sum of the even terms is 96. Find
(a) the first term and the common difference,
(b) the last term.
Solution:
(a) Let the first term = a
Common difference = d
Given the sum of the even terms = 96
(2) – (1):
16d – 15d = 24 – 23.5
d = 0.5
Substitute d = 0.5 into (2):
2a + 16 (0.5) = 24
2a + 8 = 24
2a = 16
a = 8
Therefore, first term = 8 and common difference = 0.5.
(b) Last term
= T2
= 8 + 15 (0.5)
= 8 +7.5
= 15.5

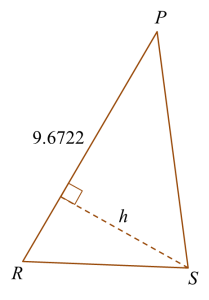
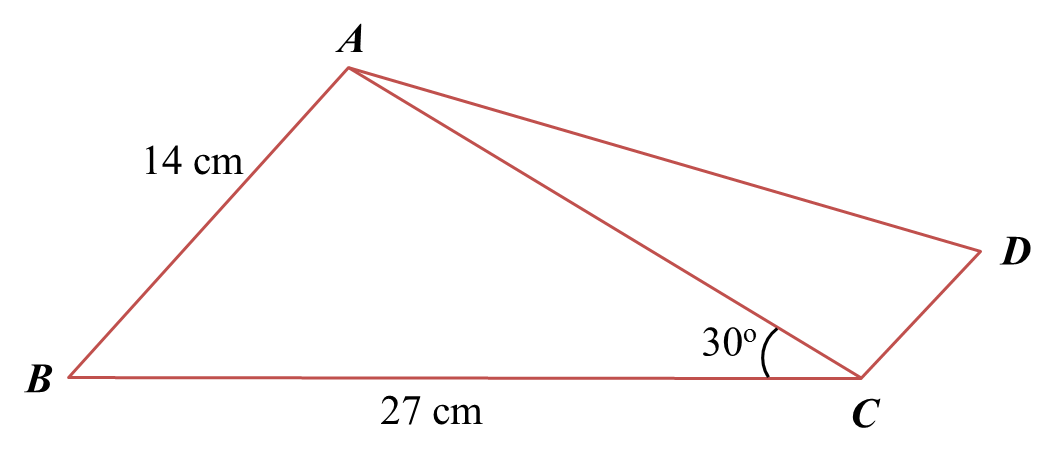

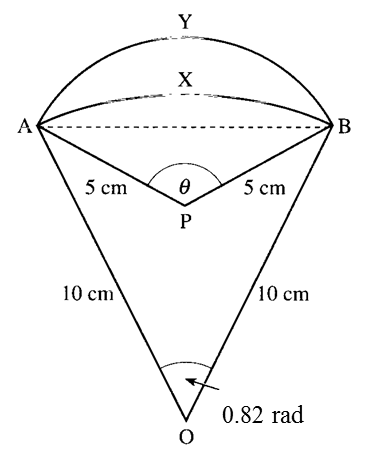
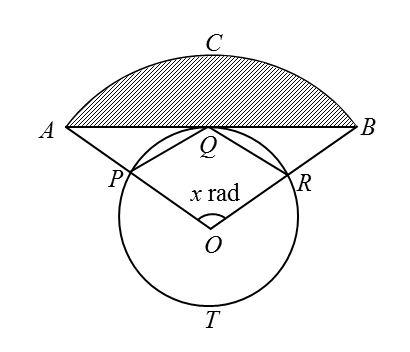 Calculate
Calculate
 [Use π = 3.142]
[Use π = 3.142]