Skip to content
Skip to main menu
- Each cell consists of a plasma membrane and protoplasm
- The protoplasm consist of cytoplasm and nucleus.
- Cytoplasm contains many types of organelles.
- The following is the illustration of the animal cell and plant cell.
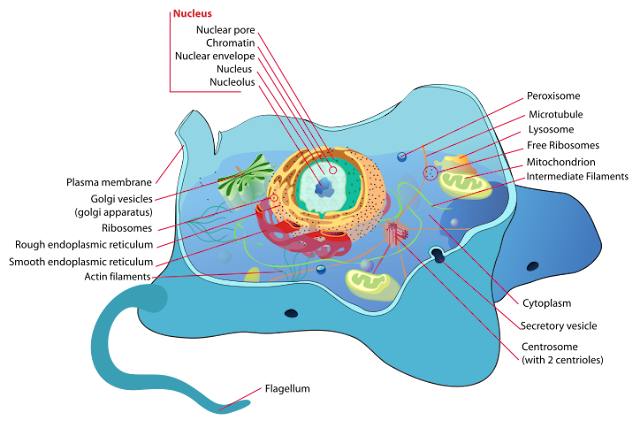 |
| (Animal Cell) |
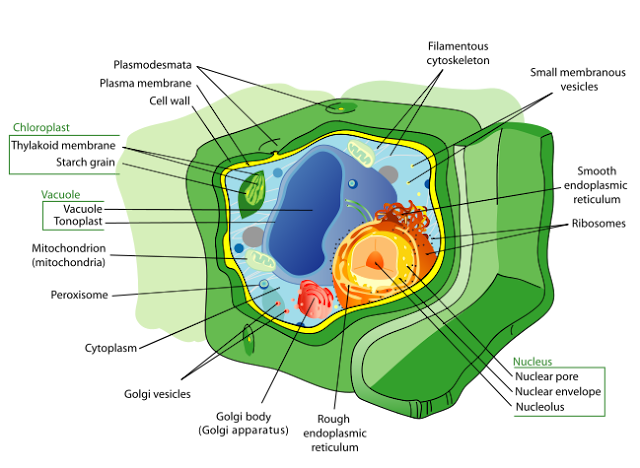 |
| (Plant Cell) |
Non-Organelle
Plasma Membrane
- The plasma membrane separates the content of the cell from its external environment.
- It regulates the movement of substances entering and leaving the cell.
- It also allows the exchange of nutrients, respiratory gases and wastes products between the cell and its environment
Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm contain variety of organelle.
- The function of the cytoplasm is to maintain the shape of the cell.
- It acts as a medium for the biochemical reactions occur within the cell
- It also store chemical substances such as glicogen granules (in animal cells), starch granules (inplant cells) and enzymes.
Cell Wall
- The cell wall only contain in plant cell. It support the cell and the plant and maintain the shape of the cell.
- It also prevents the cell from bursting when too much water enters the cell through osmosis.
- It allows substances to move through it.
Nucleus
- The nucleus contains the genetic material of a cell.
- It controls the activities of the cell.
- It also produces ribosomes and ribonucleic acids(RNA).
Organelle
Endoplasmic Recticulum (ER)
- Rough Endoplasmic Recticulum:
- Transporting the newly synthesised protein.
- Involve in the systhesis of protein.
- Provides surface for chemical reaction
- Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum:
- Transporting lipids and glycerols.
- Synthesising lipids and other non-protein substances.
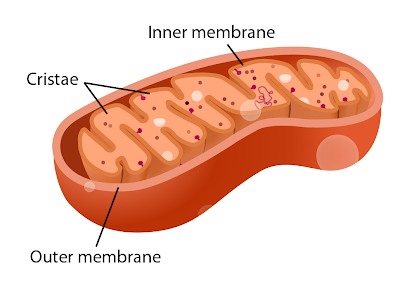
Mitochonrion
- Produces ATP (Adenosine triphosphate.)
- Site of energy production through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes
- Site for synthesising protein.
- Golgi Apparatus
- Site for the production of enzyme andlysosome.
- Produces polysacharides, glycoproteins andsecretory enzyme.
- Storing and modifying carbohydrate and glycoprotein.
- Transport and store lipid.
Vacuole
- Stores food (Carbohydrate, amino acid) and water.
- Support herbaceous plants when it is turgid.
- Stores organic waste (in leaf cells).
Chloroplast
- Contain chlorophyll and hence a site for photosynthesis to take place.
Centrosome
- The centrosome is served as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression.
- It form spindle fibres during cell division in animal cell.
Lysosomes
- Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes that digest or break down complex organic molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides and lipids.
- The enzymes eliminate worn out organelles and damaged organelles.
Golgi Apparatus
- The golgi apparatus processes proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum
- The products are sorted by the Golgi Apparatus and packaged into vesicles
- The vesicles then release their contents outside the cell.
- It also responsible to the formation of lysosomes.