Example 1:
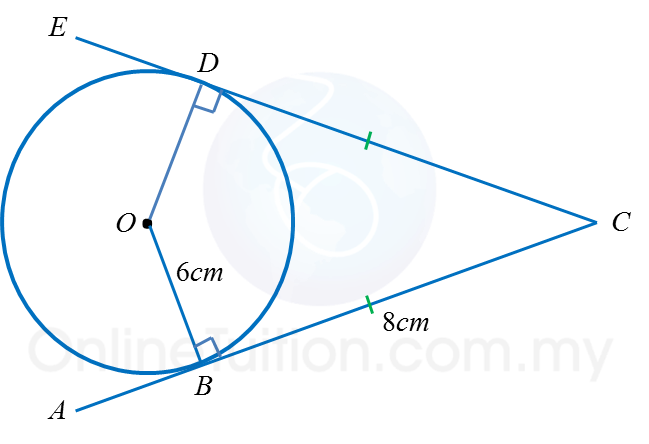 In the diagram, O is the centre of a circle. ABC and CDE are two tangents to the circle at points B and D respectively. Find the length of OC.
In the diagram, O is the centre of a circle. ABC and CDE are two tangents to the circle at points B and D respectively. Find the length of OC.
Example 2:
(b)
 In the diagram, O is the centre of a circle. ABC and CDE are two tangents to the circle at points B and D respectively. Find the length of OC.
In the diagram, O is the centre of a circle. ABC and CDE are two tangents to the circle at points B and D respectively. Find the length of OC.Solution:
OC2= OB2 + BC2 ← (Pythagoras’ Theorem)
= 62 + 82
= 100
OC = √100 = 10 cm
Example 2:

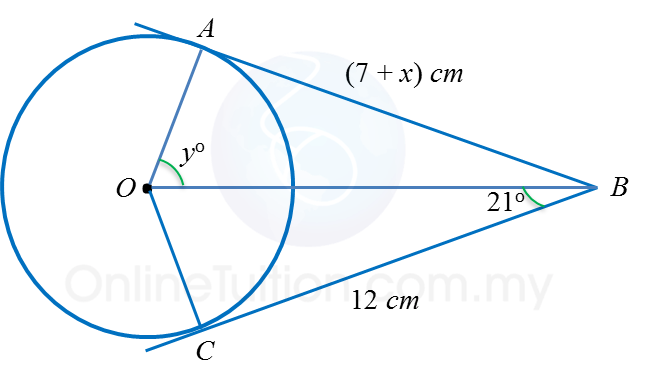
In the diagram, AB and BC are two tangents to a circle with centre O. Calculate the values of
(a) x (b) y
Solution:
(a)
AB = BC
7 + x = 12
x = 5
(b)
∠
OBA =
∠
OBC = 21o
∠
OAB = 90o ← (OA is perpendicular to AB)
yo= 180o – 21o – 90o
y = 69Example 3:
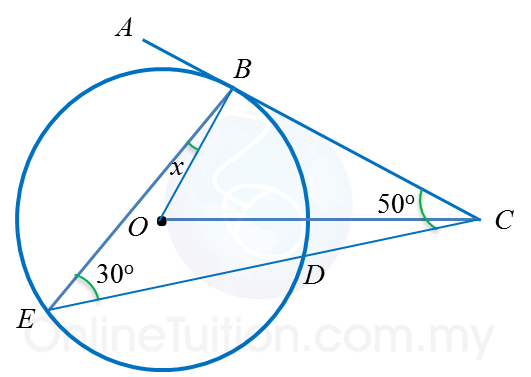

In the diagram, ABC is a tangent to the circle with centre Oat point B. CDE is a straight line. Find the value of x.
Solution:
∠
CBO = 90o ← (OB is perpendicular to BC)
In ∆ BCE,
x = 180o – 30o – 50o– 90o
x = 10o

 (a) Using data in diagram above and a class interval of 5 marks, complete the table in the answer space.
(a) Using data in diagram above and a class interval of 5 marks, complete the table in the answer space.



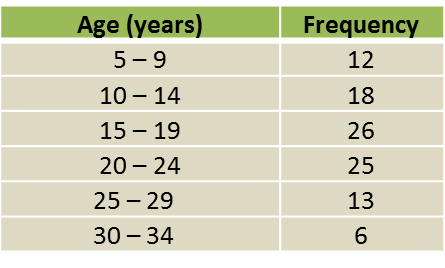
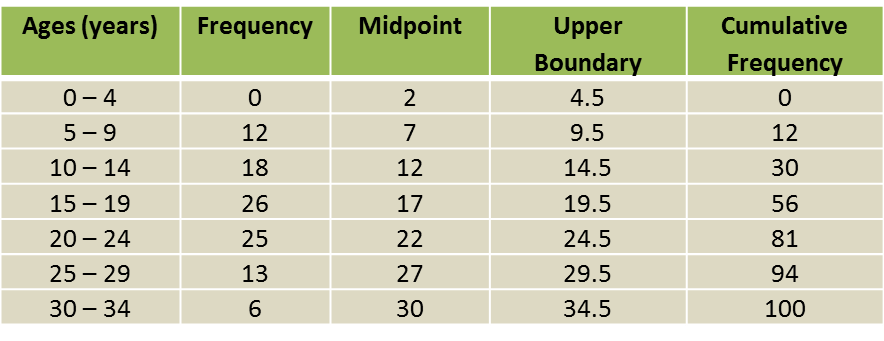
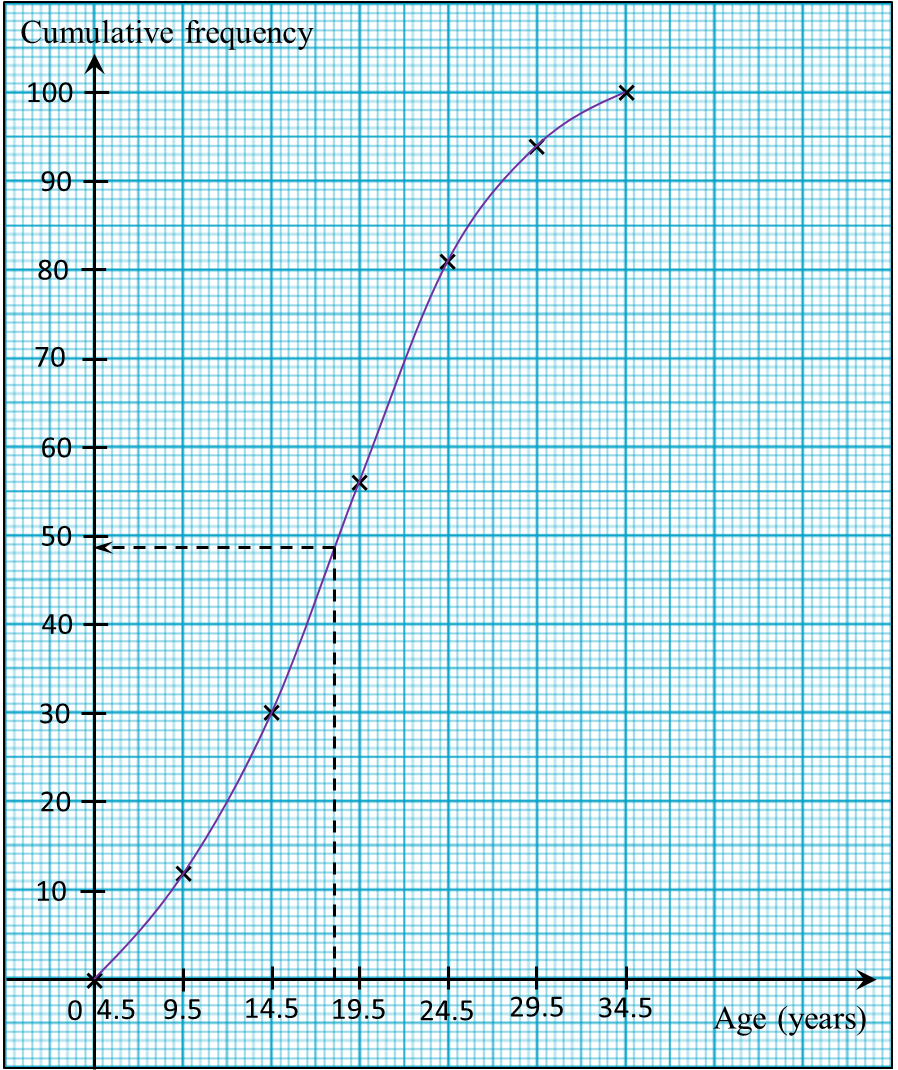
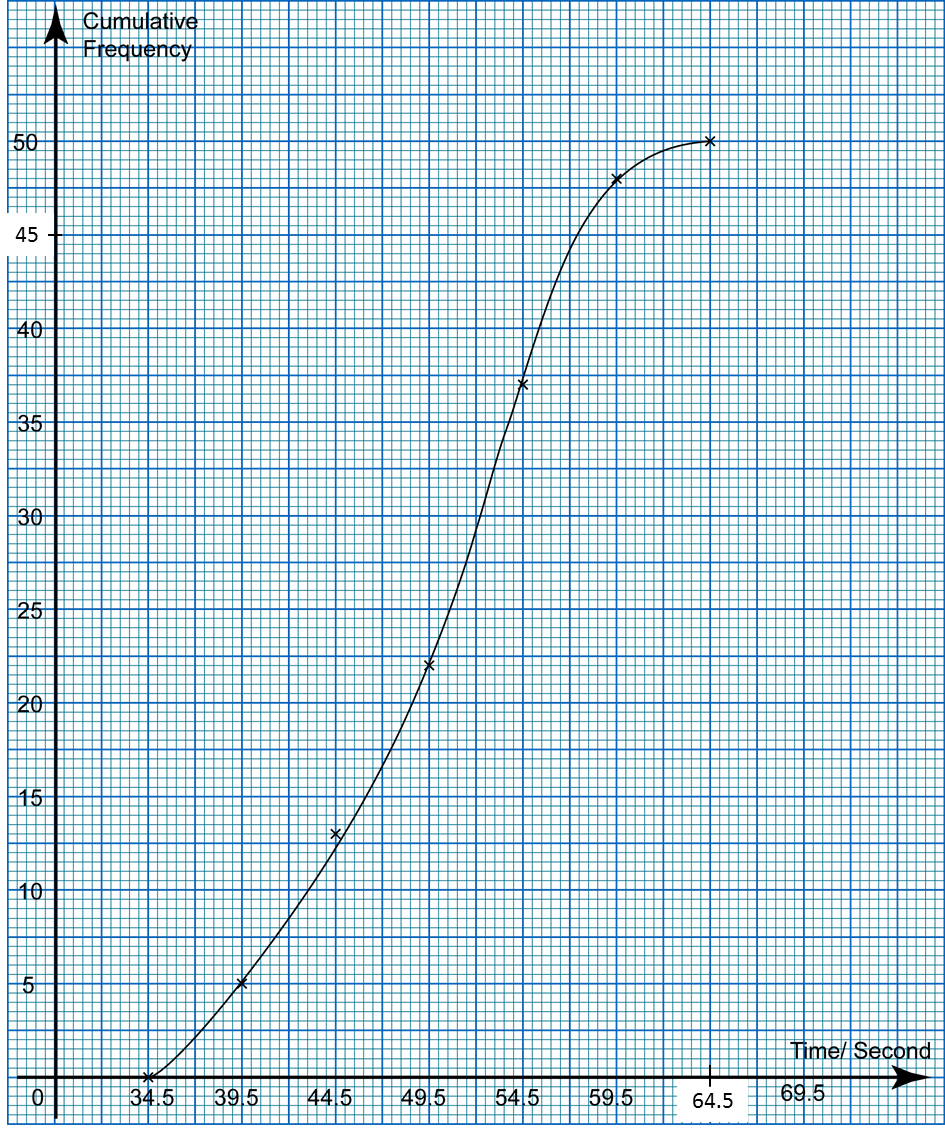
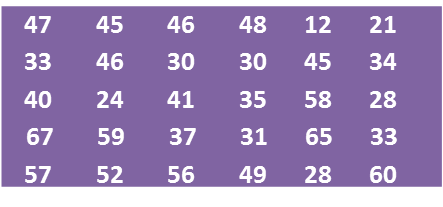
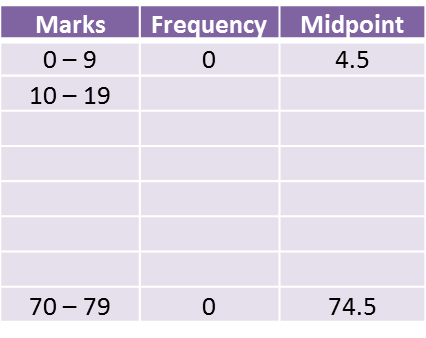
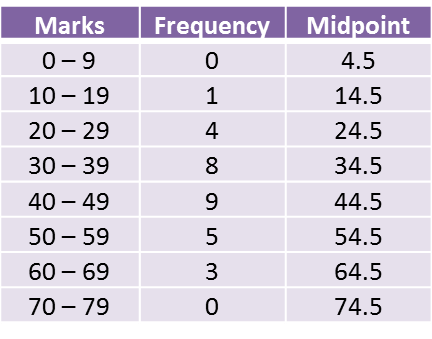
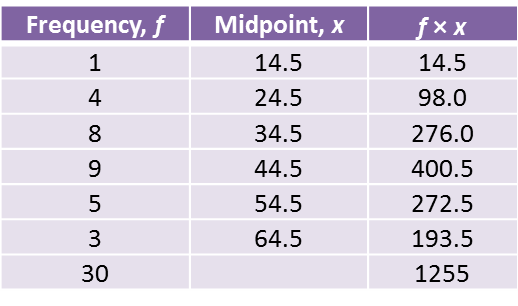
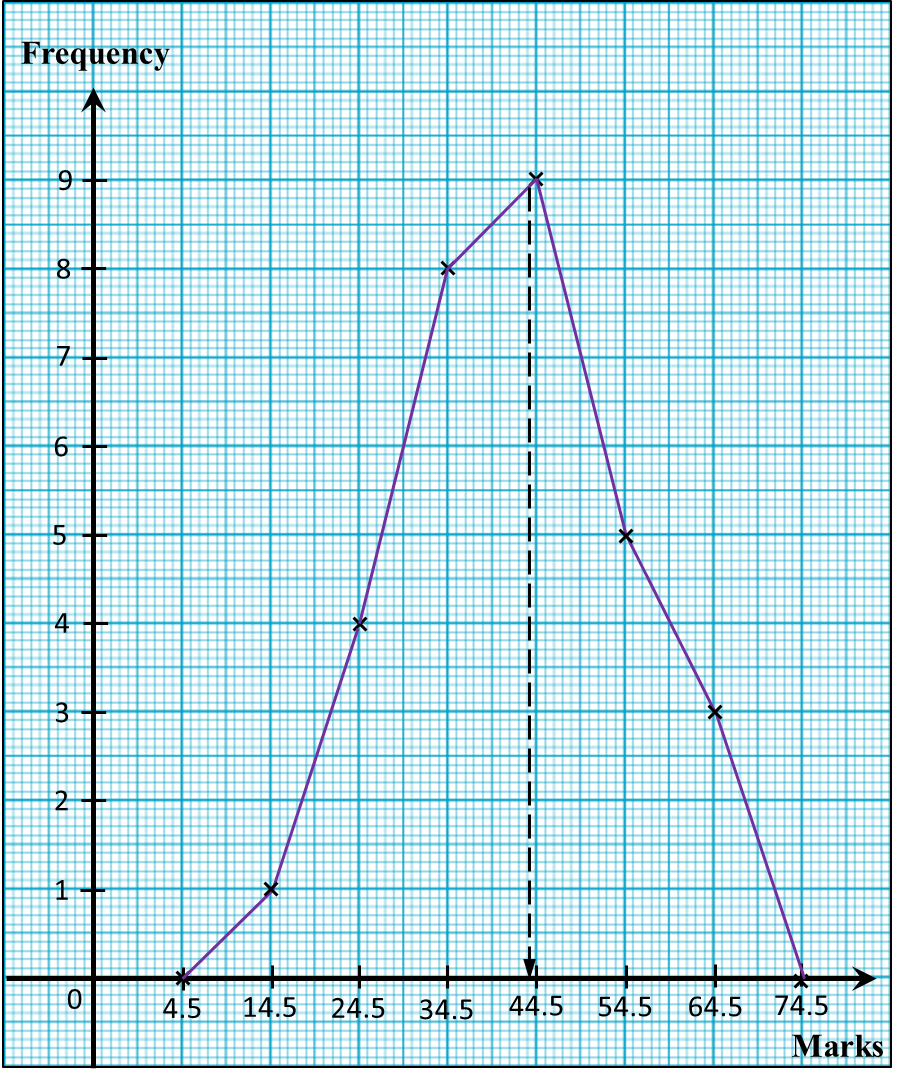
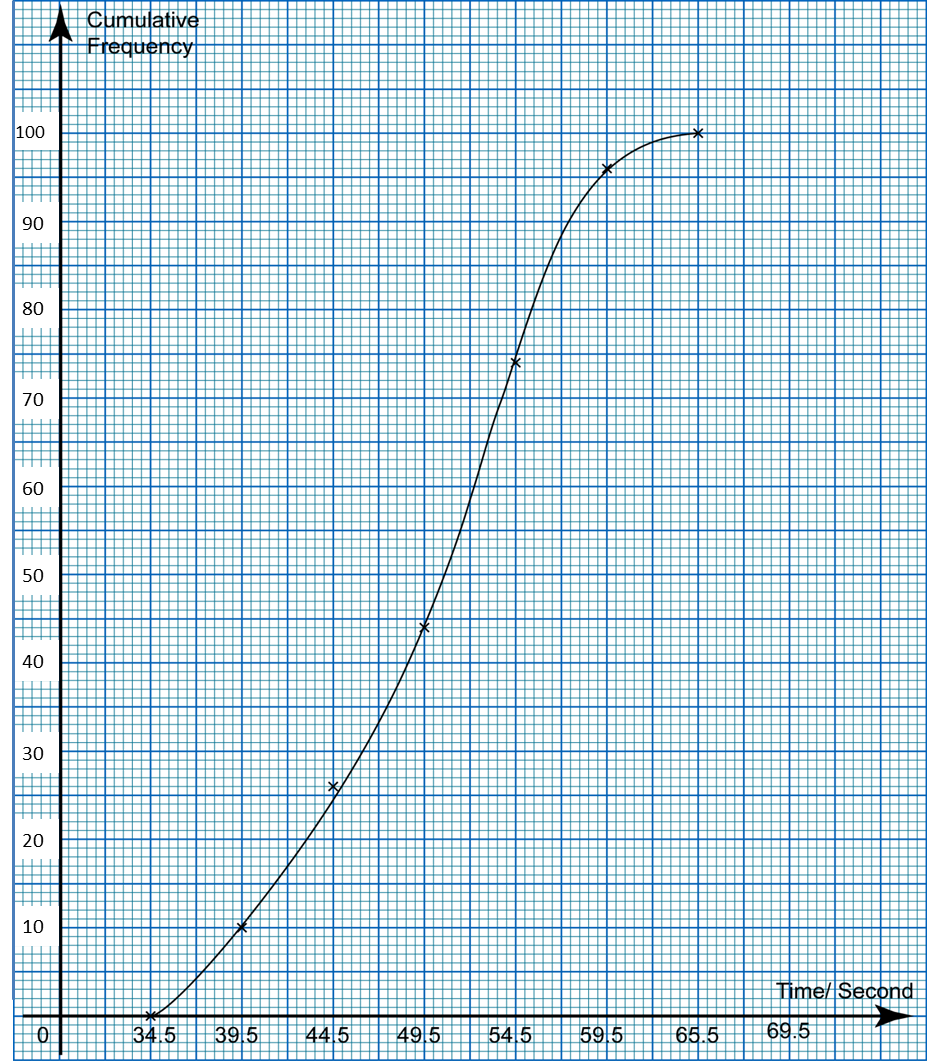
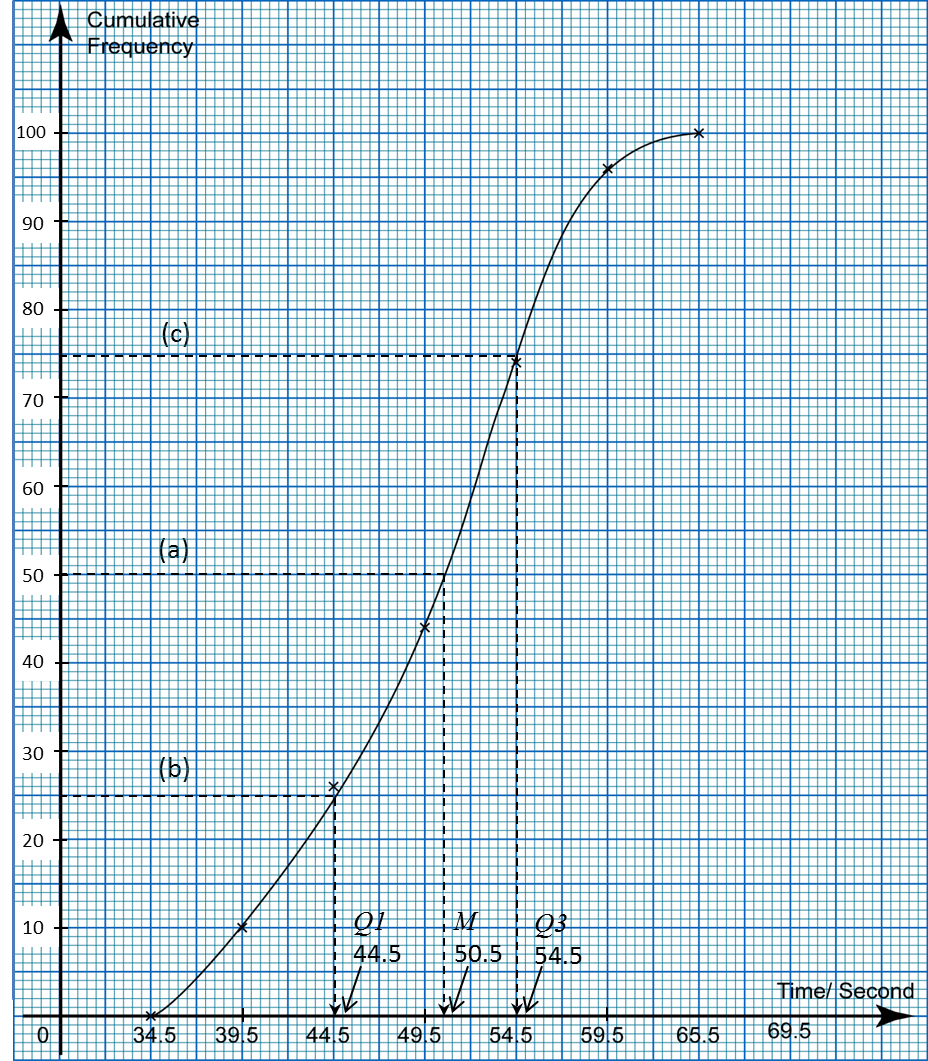
 Diagram 6
Diagram 6