Question 10 (3 marks):
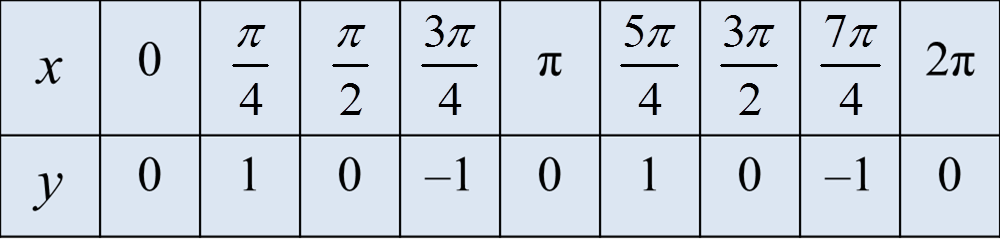
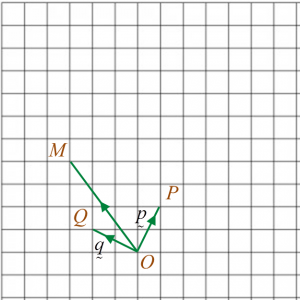
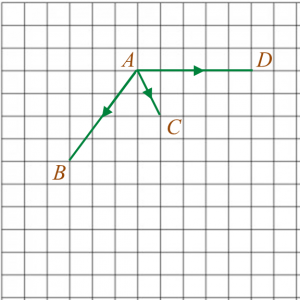
Diagram 3 shows vectors →OP, →OQ and →OM drawn on a square grid.
 Diagram
Diagram
(a) Express →OM in the form hp˜+kq˜, where h and k are constants.(b) On the diagram 3, mark and label the point N such that →MN+→OQ=2→OP.
Solution:
(a)
→OM=p˜+2q˜
(b)
→MN+→OQ=2→OP→MN=2→OP−→OQ =2p˜−q˜
Diagram 3 shows vectors →OP, →OQ and →OM drawn on a square grid.
 Diagram
Diagram(a) Express →OM in the form hp˜+kq˜, where h and k are constants.(b) On the diagram 3, mark and label the point N such that →MN+→OQ=2→OP.
Solution:
(a)
→OM=p˜+2q˜
(b)
→MN+→OQ=2→OP→MN=2→OP−→OQ =2p˜−q˜
Question 11 (4 marks):
A(2, 3) and B(−2, 5) lie on a Cartesian plane.It is given that 3→OA=2→OB+→OC.Find(a) the coordinates of C,(b) |→AC|
Solution:
Given A(2,3) and B(−2,5)Thus, →OA=2i˜+3j˜ and →OB=−2i˜+5j˜
(a)
3→OA=2→OB+→OC→OC=3→OA−2→OB =3(2i˜+3j˜)−2(−2i˜+5j˜) =6i˜+9j˜+4i˜−10j˜ =10i˜−j˜Thus, coordinate of C is (10, −1)
(b)
→AC=→AO+→OC =−→OA+→OC =−(2i˜+3j˜)+10i˜−j˜ =−2i˜+10i˜−3j˜−j˜ =8i˜−4j˜|→AC|=√82+(−4)2 =√80 units =√16×5 units =4√5 units
A(2, 3) and B(−2, 5) lie on a Cartesian plane.It is given that 3→OA=2→OB+→OC.Find(a) the coordinates of C,(b) |→AC|
Solution:
Given A(2,3) and B(−2,5)Thus, →OA=2i˜+3j˜ and →OB=−2i˜+5j˜
(a)
3→OA=2→OB+→OC→OC=3→OA−2→OB =3(2i˜+3j˜)−2(−2i˜+5j˜) =6i˜+9j˜+4i˜−10j˜ =10i˜−j˜Thus, coordinate of C is (10, −1)
(b)
→AC=→AO+→OC =−→OA+→OC =−(2i˜+3j˜)+10i˜−j˜ =−2i˜+10i˜−3j˜−j˜ =8i˜−4j˜|→AC|=√82+(−4)2 =√80 units =√16×5 units =4√5 units
 Diagram
Diagram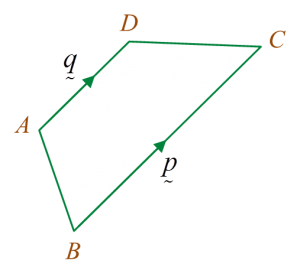 Diagram
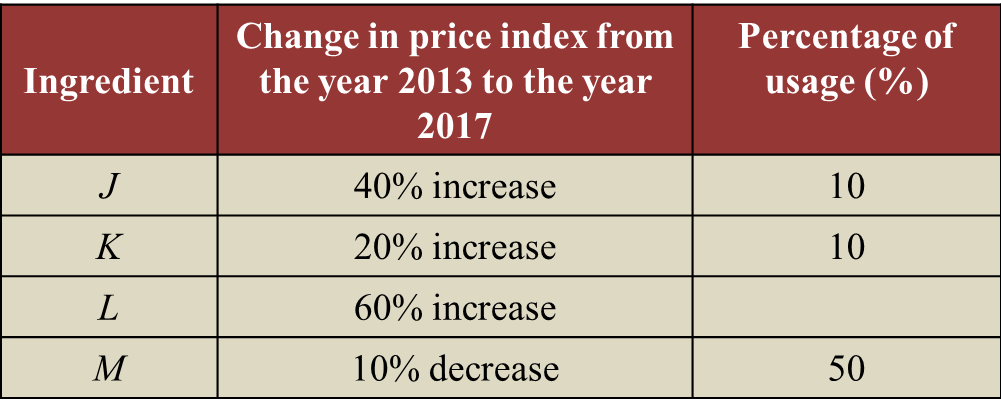
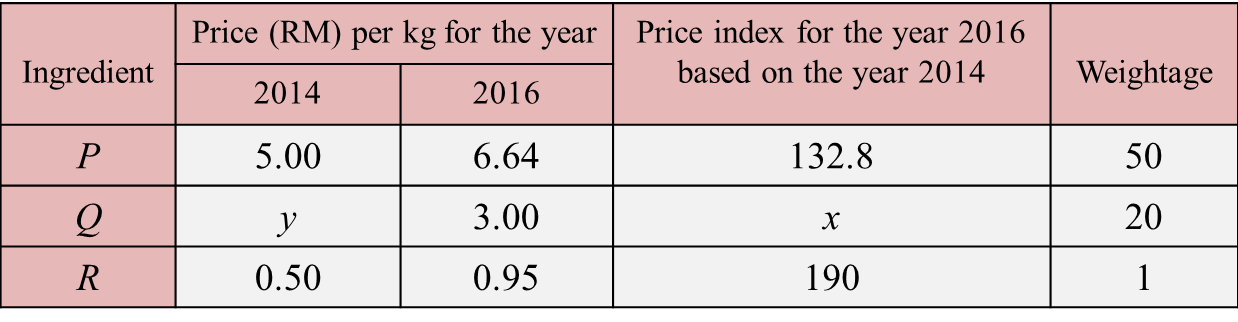
Diagram Table
Table 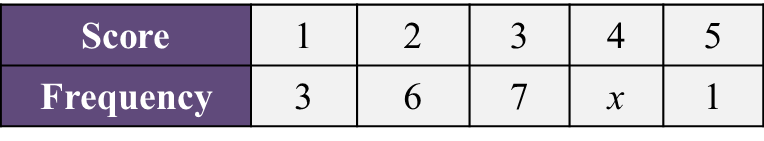 Table
Table 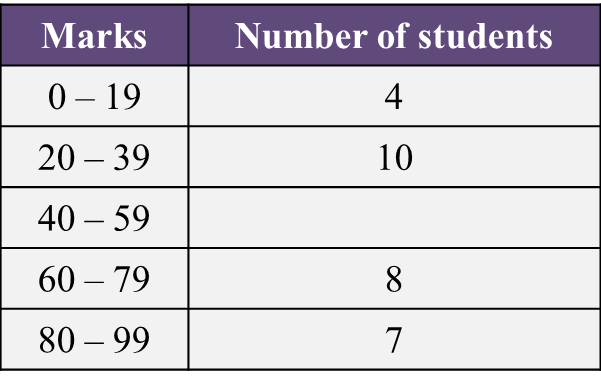 Table
Table Diagram
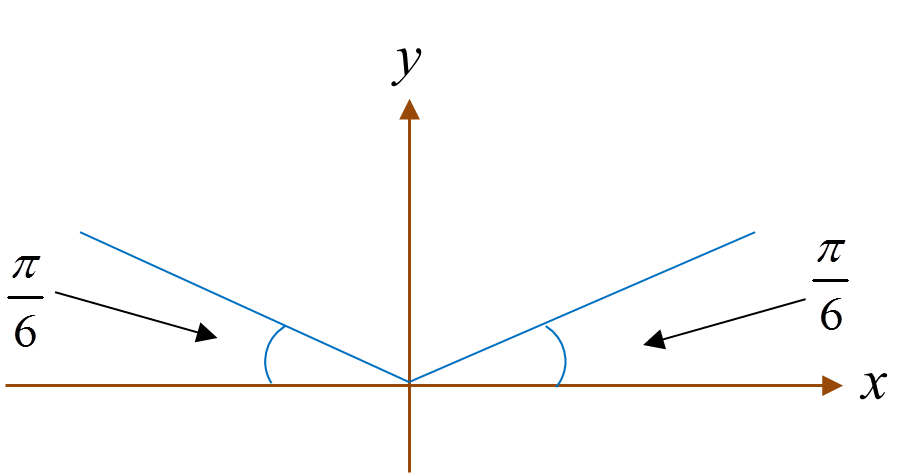
Diagram  Diagram
Diagram  Diagram
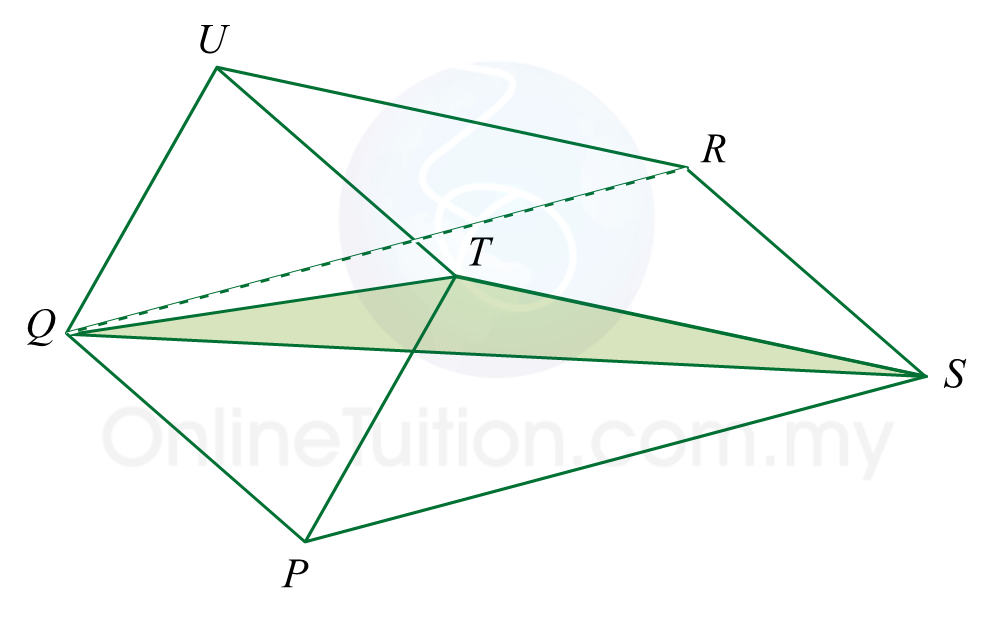
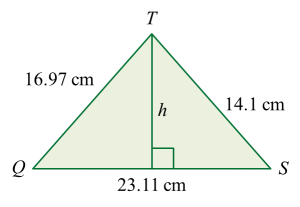
Diagram  VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.
VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.