[adinserter block="3"]
Question 7:
Diagram 7.1 shows the parts of blood circulatory and lymphatic system in human.
 Diagram 7.1
Diagram 7.1
(a) Explain how fluid Q is formed. [4 marks]
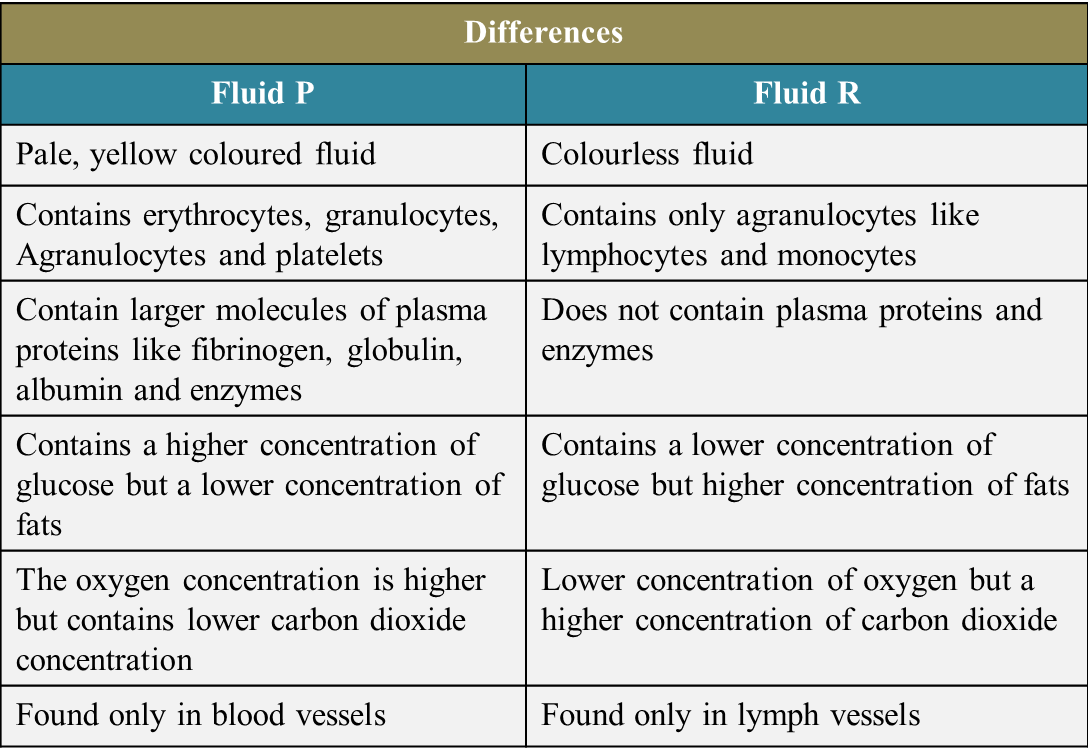
(b) Describe similarities and differences between fluids P and R. [10 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
(c) Diagram 7.2 shows a type of worm which is transmitted by mosquitoes to human. The mosquito is the vector of disease X.
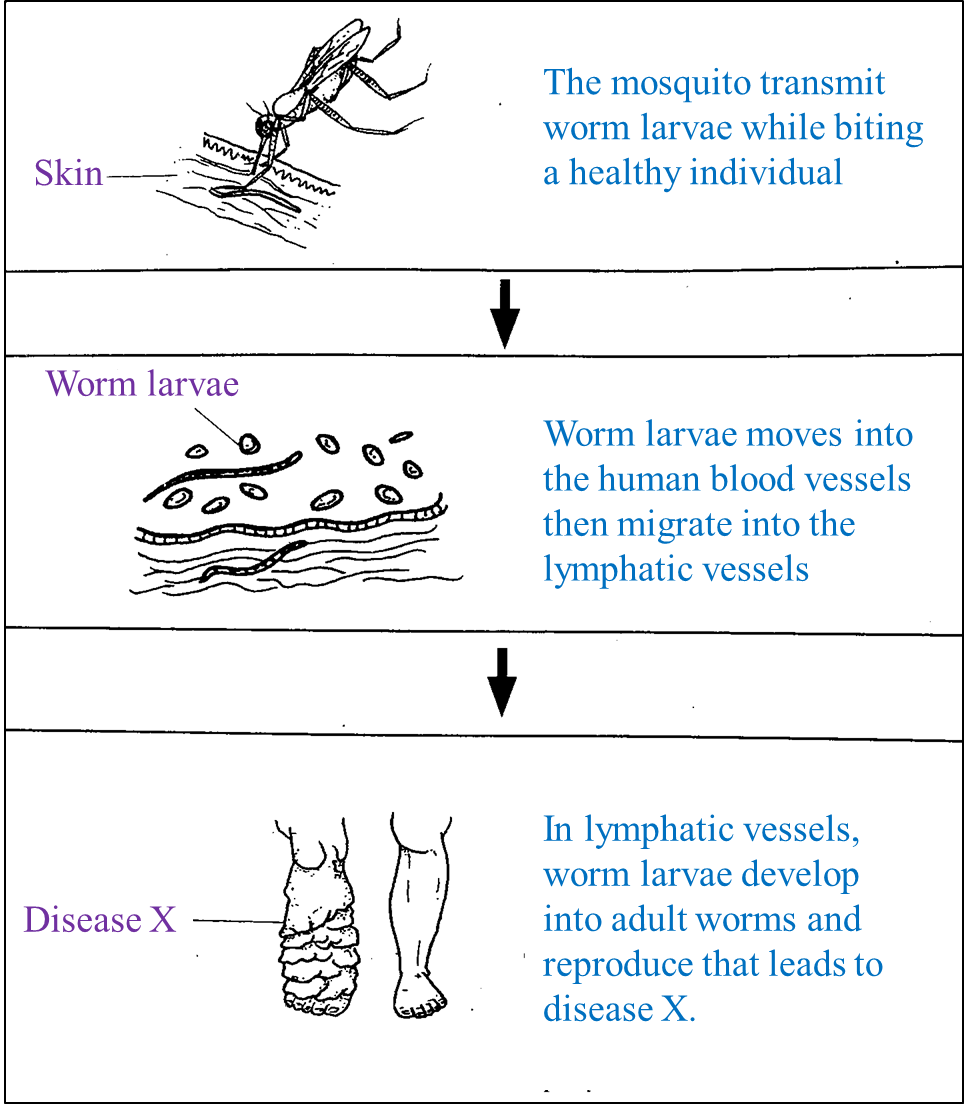 Diagram 7.2
Diagram 7.2 Discuss how disease X occurs.
Suggest ways to prevent the disease. [6 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)- Fluid Q is the interstitial fluid / tissue fluid.
- It is formed from blood plasma.
- When blood flows through the capillaries, the higher blood pressure at the arterial end of the blood capillary network causes blood plasma to diffuse out into the intercellular spaces.
- This fluid that fills the intercellular spaces is termed the interstitial fluid.
(b)
Similarities:
1. Both blood plasma and lymph are pale coloured fluids.
2. Both the fluids are aqueous solutions containing various types of solute molecules.
3. Like glucose, amino acids, lipids, respiratory gases and antibodies.
4. Both the fluids contain agranulocytes / lymphocytes.
[adinserter block="3"]
(c)
- Disease X is usually called elephantiasis / filariasis.
- The disease is caused by filarial worms which become lodged in lymph nodes and block the flow of lymph fluid.
- The microscopic worms are spread by mosquitoes / Cules Mosquitoes.
- The mosquitoes suck the microscopic worms when they feed on blood of an infected person.
- The worms are then transmitted into blood of another person when the mosquito bites to suck blood.
- The microscopic worms migrate into the lymph vessels and live in the lymph nodes. Here the worms grow, reach adulthood and breed.
- The worms block the flow of lymph fluid, causing a higher hydrostatic pressure to build up within the lymph vessels.
- Interstitial fluid accumulates in the intercellular spaces and cause swelling of the legs/ arms/ breast/ testicles.
- The skin in the swollen region becomes dry and scaly and pored/ tears. The condition causes severe pain.
- Ways to prevent the disease:
1. Avoid being bitten by mosquitoes
- Sleeping with mosquito netting
- Wearing clothing to cover the body when in outdoors
- Applying / using mosquito repellents.
2. Destroy breeding grounds of mosquitoes like preventing accumulation of water in rubbish bins and containers.
3. Kill adult mosquitoes by fumigation, mosquito larvae by spraying insecticide or petroleum oil on water surfaces of stagnant water.
[adinserter block="3"]
Question 8:
(a) The wife of a newly married couple is diagnosed with an inheritance disease. If this couple had children, the children might have genetic disorder. The doctor advised her to use some birth control methods.
Table 8.1 shows the comparison of some birth control methods.
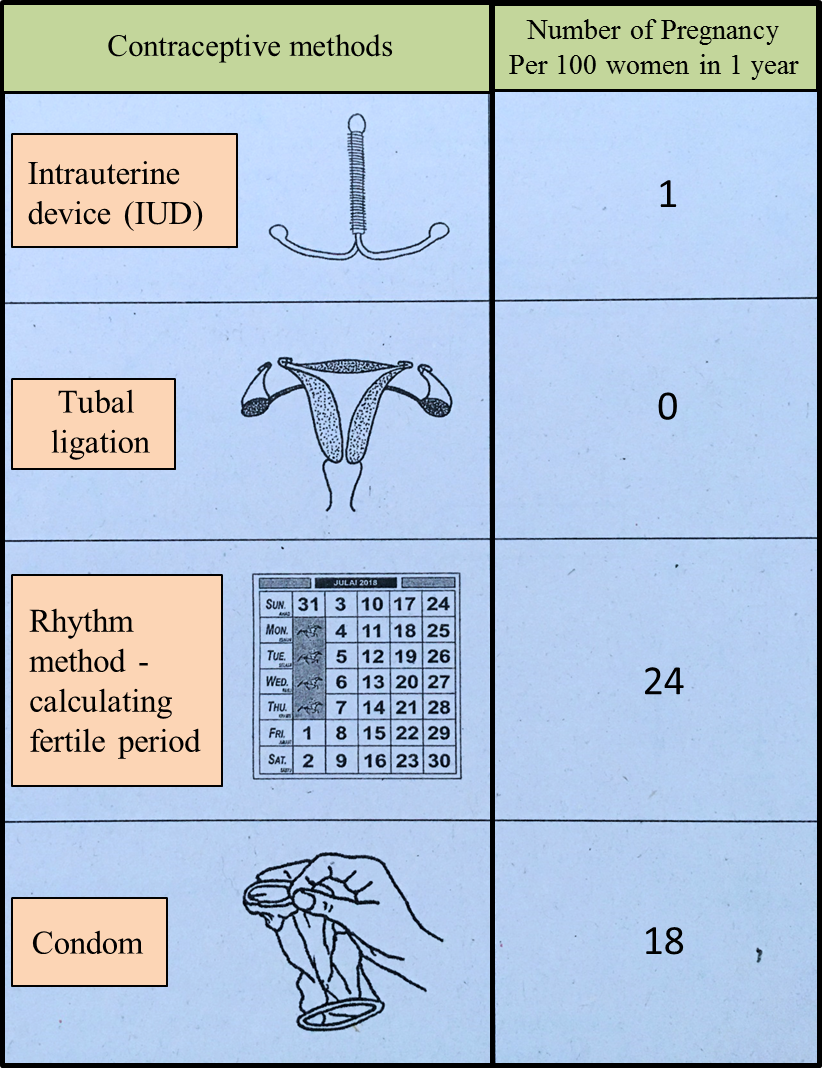 Table 8.1(i)
Table 8.1(i) Based on Table 8.1, choose the best two effective methods to prevent pregnancy.
Explain your reasons.
(ii) Beside the contraceptive methods in Table 8.1, the consumption of contraceptive pills is also being practised.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of this contraceptive method.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b) A flower is the reproductive organ for a plant. Fertilization process occurs in the ovule to form a fruit. The fruit is the ripened ovary of a flower.
Diagram 8.2 shows the process of a flower which turn into a fruit.
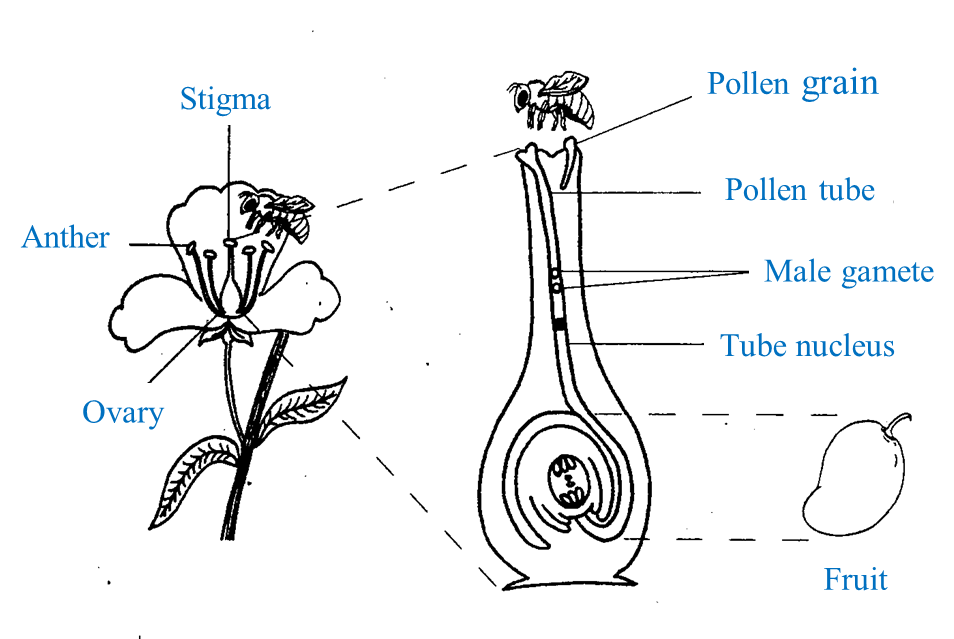 Diagram 8.2
Diagram 8.2Based on Diagram 8.2 explain how a fruit is formed from a flower.
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)(i)- The two effective methods to prevent pregnancy are the use of intrauterine device (IUD) and tubal ligation.
- IUD – A loop made of plastic or copper is inserted into the uterus by a doctor / trained medical nurse.
- The ovum is prevented from being fertilized by preventing the sperm from reaching the ovum.
- It is highly effective as the chance of pregnancy is only 1%.
- The Fallopian tube is clamped / cut and sealed in the surgical procedure
- The ovum is prevented from entering the Fallopian tube, hence there will be no fertilization
- It is very effective method as there is 0% pregnancy
[adinserter block="3"]
(a)(ii)
Advantages
- An easy method to prevent pregnancy without the use of physical devices like IUD, uterine diaphragm, condom
- Menstrual flow is lighter
- Menstruation becomes regular
- Avoids menstrual cramps
Disadvantage
- May use vaginal bleeding / spotting
- Missed menstrual periods
- Dizziness, headache
- Breast tenderness
- Enlargement of breasts
- Body weight gain
- Mood swings
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)
- During pollination, mature pollens land on stigma.
- Each pollen contains a generative nucleus and a tube nucleus.
- The stigma secretes sugary fluid which induces the germination of the pollen.
- Tube nucleus directs the formation of pollen tube.
- The tube nucleus and generative nucleus move into the pollen tube.
- The pollen tube grows through the style and reaches the micropyle of the ovule.
- The tube nucleus breaks down just before the pollen tube reaches the ovule.
- The generative nucleus divides once by mitosis to form two male nuclei.
- The pollen tube enters the ovule through the micropyle and its tio dissolves to release the two male nuclei.
- One of the male nuclei fuses with the two haploid polar nuclei in the embryo sac to form a triploid cell called the endosperm.
- The other male nucleus fuses with the egg cell nucleus to form the diploid zygote.
- This phenomenon is termed double fertilization which induces the following changes and developments within the flower, resulting in the formation of fruit and seed.
- The ovary of the flower develops into the fruit.
- The ovules form the seeds.
- The zygote in the seed develops into the embryo and endosperm develops into the nutritive endosperm tissue, surrounding the embryo.
- The sepals and style dry up and form scar tissues of the fruit.
- The petals dry and wither-off.
- The flower stalk becomes the fruit stalk.


 Diagram 9
Diagram 9 Diagram 7
Diagram 7 Table 2
Table 2 Diagram 8
Diagram 8 Diagram 7.1
Diagram 7.1  Diagram 7.2
Diagram 7.2 
 Table 8.1
Table 8.1 Diagram 8.2
Diagram 8.2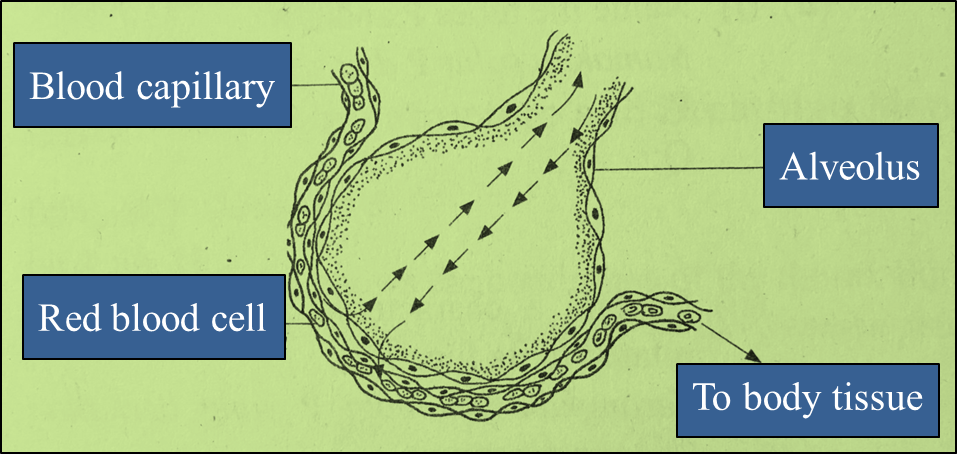 Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.1
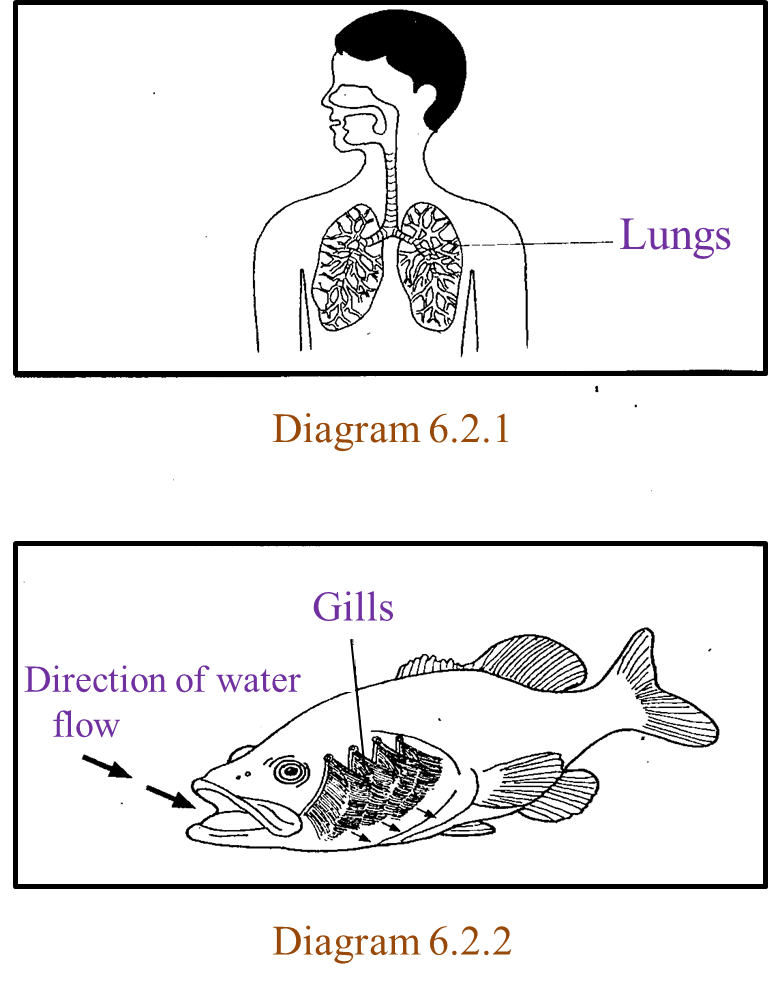
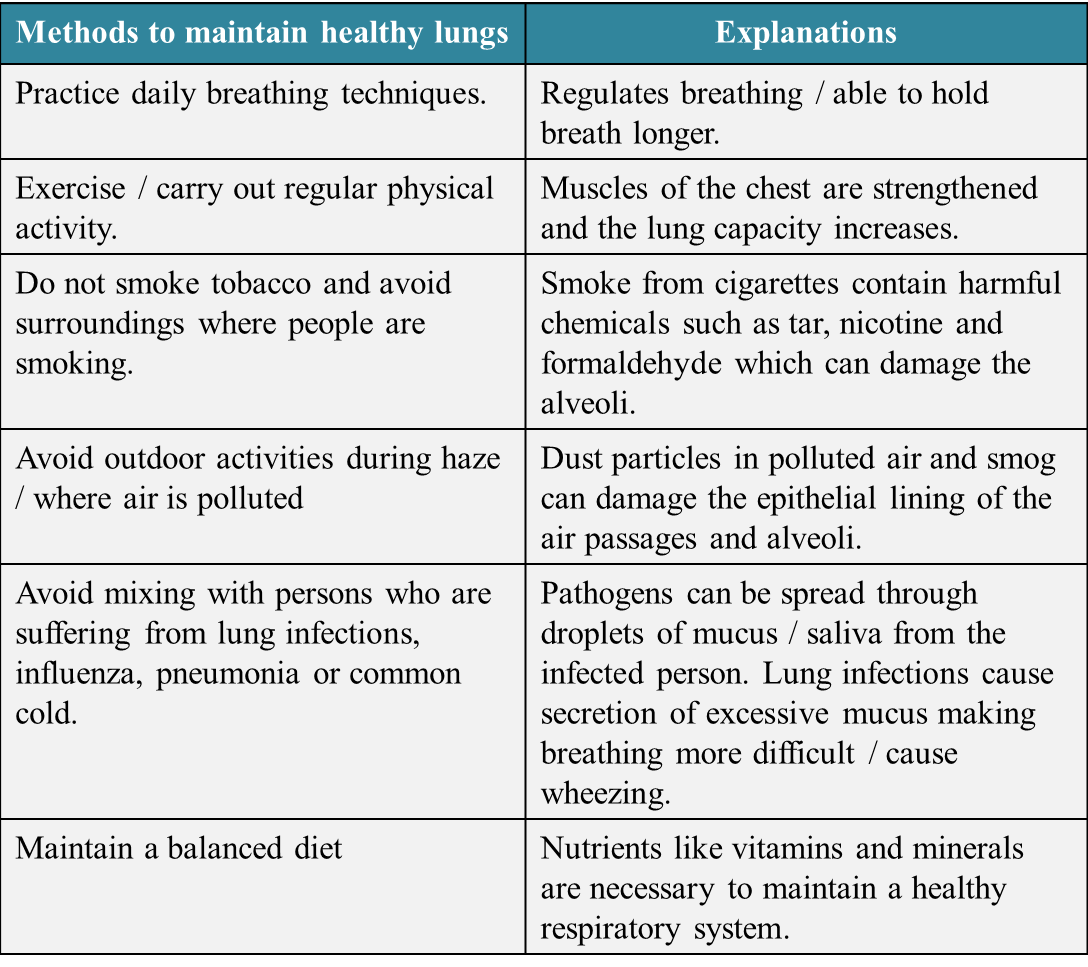
 Diagram 5
Diagram 5
 Diagram 6
Diagram 6

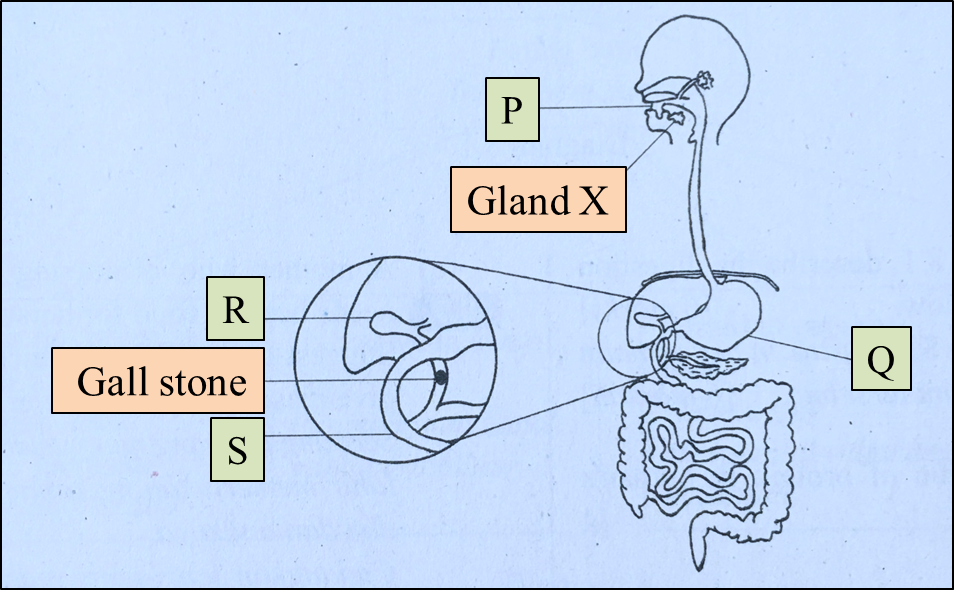 Diagram 3
Diagram 3 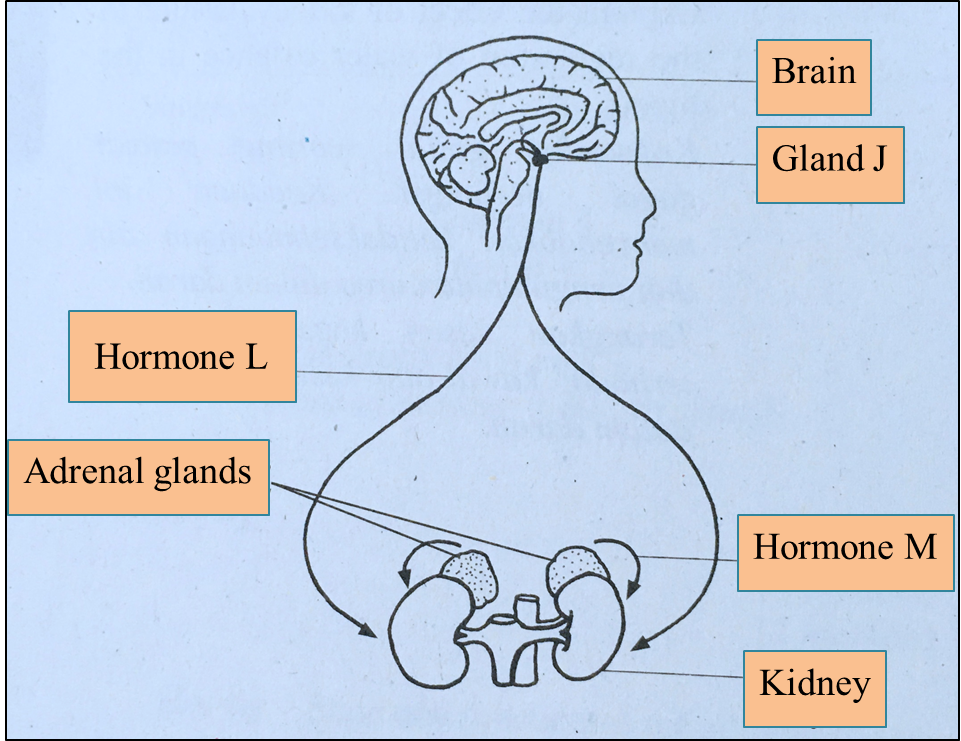 Diagram 4.1
Diagram 4.1
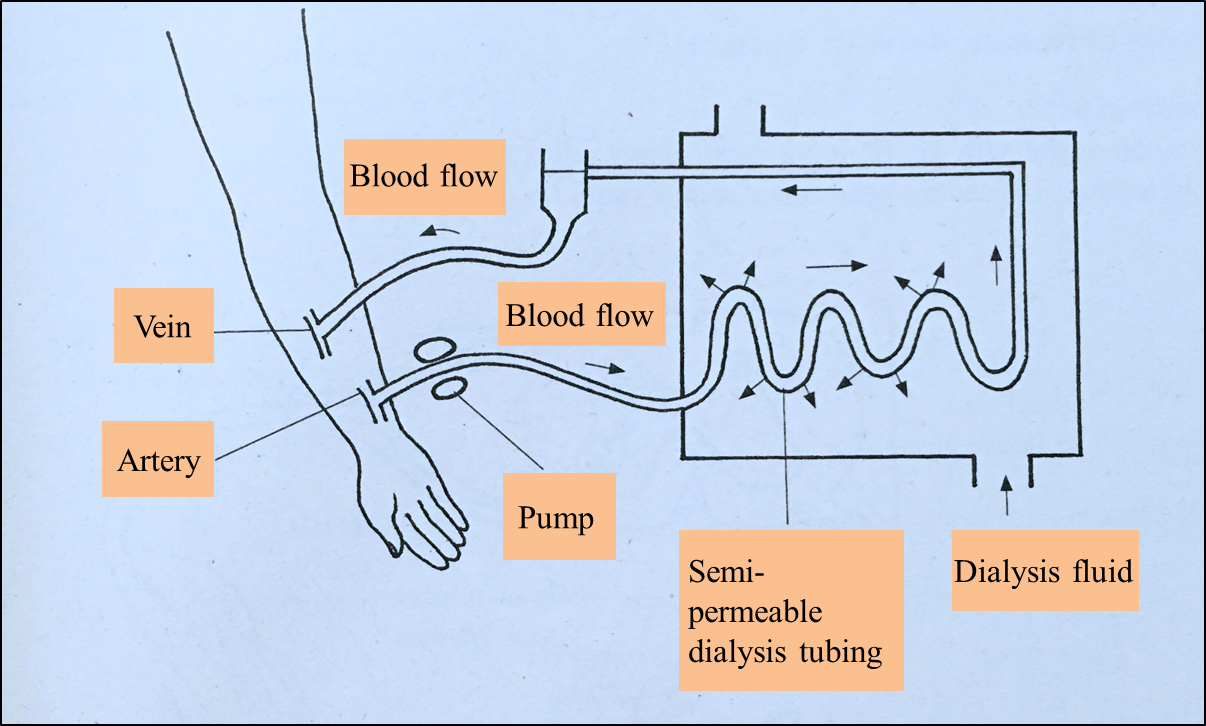 Diagram 4.2
Diagram 4.2