[adinserter block="3"]
Question 3:
Diagram 3 shows two types of hair which are curly and straight hair for 30 customers at a saloon.

Diagram 3
(a) Based on Diagram 3, complete Table 1. [2 marks]
 Table 1
Table 1
[adinserter block="3"]
(b) Based on Table 1, draw a bar chart to show the number of customers against the types of hair. [2 marks]

(c) Based on bar chart in 3(b), state the type of variation. [1 mark]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)

[adinserter block="3"]
(b)

(c) Discontinuous variation
Diagram 3 shows two types of hair which are curly and straight hair for 30 customers at a saloon.

Diagram 3
(a) Based on Diagram 3, complete Table 1. [2 marks]
 Table 1
Table 1[adinserter block="3"]
(b) Based on Table 1, draw a bar chart to show the number of customers against the types of hair. [2 marks]

(c) Based on bar chart in 3(b), state the type of variation. [1 mark]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)

[adinserter block="3"]
(b)

(c) Discontinuous variation
[adinserter block="3"]
Question 4:
Diagram 4.1 and Diagram 4.2 show an experiment to study the effect of sunlight on white photographic paper coated with argentum chloride.

[adinserter block="3"]
(a) Based on Diagram 4.1, state the colour of the photographic paper after being exposed to sunlight. [1 mark]
(b) State one inference for your answer in 4(a). [1 mark]
(c) State the variables in this experiment. [2 marks]
(i) Manipulated variable
(ii) Responding variable
(d) State the operational definition for photographic paper. [1 mark]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a) Grey
(b) Photographic paper reacts to light
(c)(i) Presence of sunlight
(c)(ii) Colour change of photographic paper
(d) Photographic paper is a paper that turns grey when exposed to sunlight
Diagram 4.1 and Diagram 4.2 show an experiment to study the effect of sunlight on white photographic paper coated with argentum chloride.

[adinserter block="3"]
(a) Based on Diagram 4.1, state the colour of the photographic paper after being exposed to sunlight. [1 mark]
(b) State one inference for your answer in 4(a). [1 mark]
(c) State the variables in this experiment. [2 marks]
(i) Manipulated variable
(ii) Responding variable
(d) State the operational definition for photographic paper. [1 mark]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a) Grey
(b) Photographic paper reacts to light
(c)(i) Presence of sunlight
(c)(ii) Colour change of photographic paper
(d) Photographic paper is a paper that turns grey when exposed to sunlight
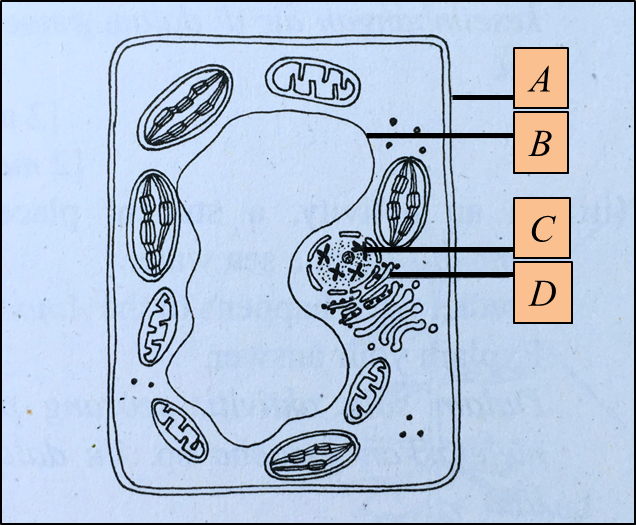 Diagram 1.1
Diagram 1.1 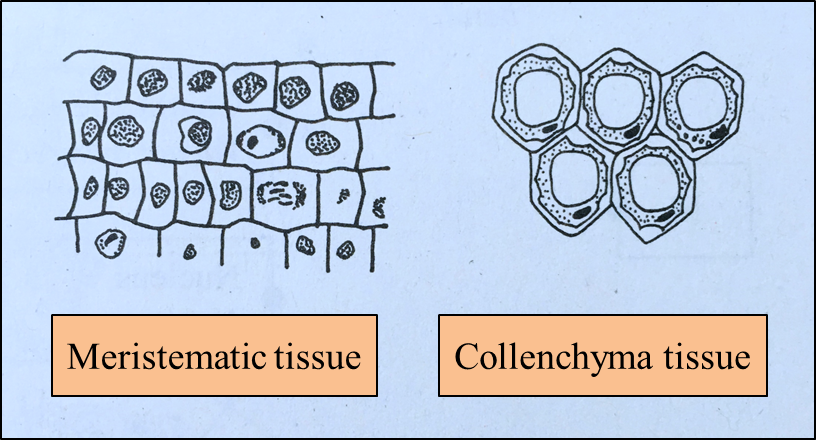 Diagram 1.2
Diagram 1.2 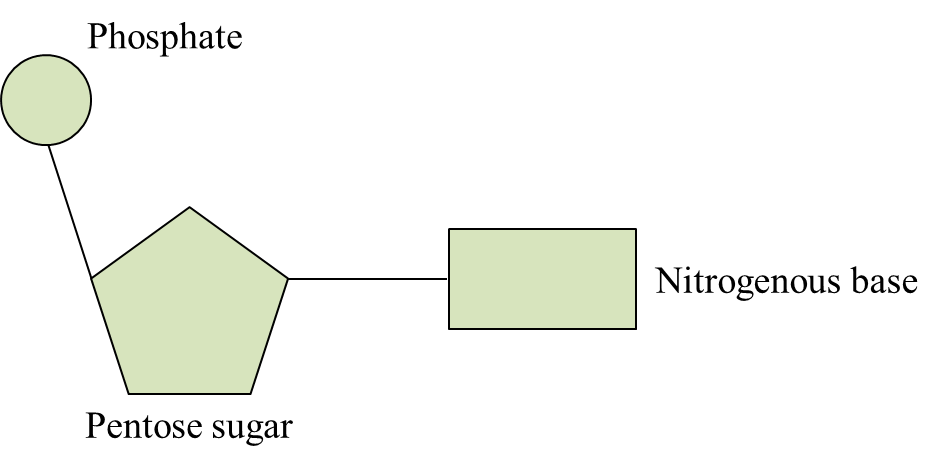
 Diagram 2.1
Diagram 2.1 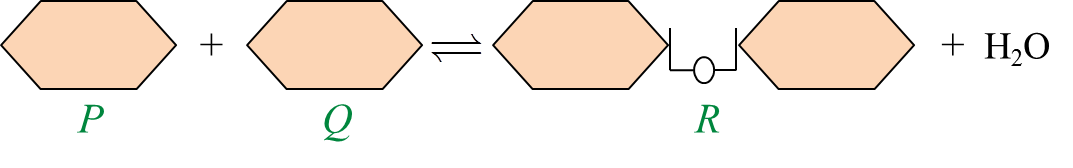 Diagram 2.2
Diagram 2.2


 Diagram 9
Diagram 9

 Diagram 7.1
Diagram 7.1 Diagram 7.2
Diagram 7.2
 Diagram 8.1
Diagram 8.1 Diagram 8.2
Diagram 8.2

 Diagram 5.1
Diagram 5.1

 Diagram 5.2
Diagram 5.2 Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.1 Diagram 6.2
Diagram 6.2 Diagram 3
Diagram 3 Diagram 1
Diagram 1 Table 1
Table 1

 Diagram 2
Diagram 2 Table 2
Table 2 (Speed is derived from dividing distance by time.)
(Speed is derived from dividing distance by time.)












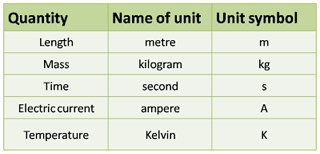 TIPS: In SPM, you MUST remember all 5 base quantities and its SI unit.
TIPS: In SPM, you MUST remember all 5 base quantities and its SI unit.