Question 10 (4 marks):
Diagram 10 shows the position of three campsites A, B and C at a part of a riverbank drawn on a Cartesian plane, such that A and B lie on the same straight riverbank.
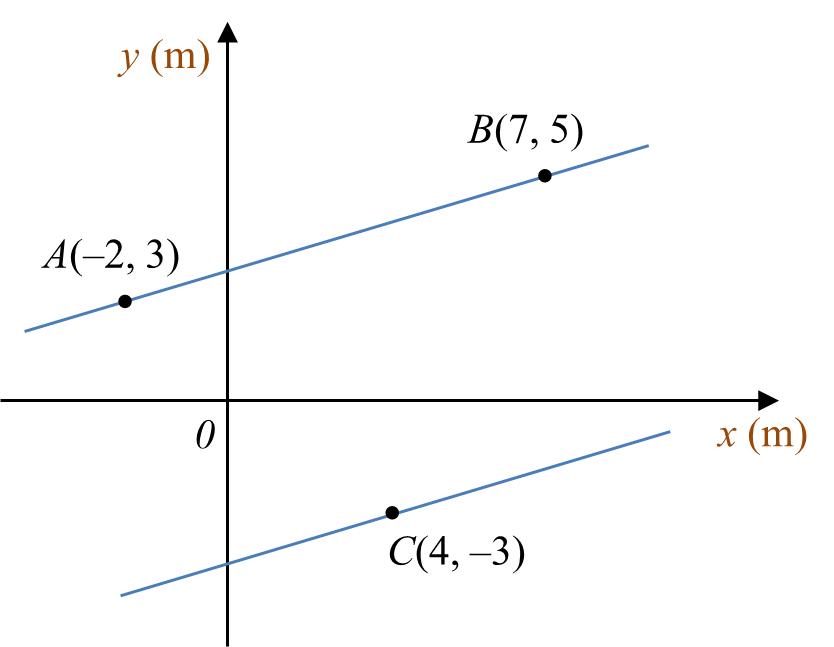 Diagram 10
Diagram 10
Sam wants to cross the river from campsite C to the opposite riverbank where the campsites A and B are located.
Find the shortest distance, in m, that he can take to cross the river. Give your answer correct to four decimal places.
Solution:
Let the shortest distance from campsite Cto opposite riverbank is CD.Area of △ABC=12|−2 7 4 3 5 −3 −2 3|=12|(−2)(5)+(7)(−3)+(4)(3)−(3)(7)−(5)(4)−(−3)(−2)|=12|−66|=33 units2Distance of AB=√(−2−7)2+(3−5)2=√85 mArea of △ABC=3312(AB)(CD)=3312(√85)(CD)=33CD=33(2)√85CD=7.1587 (4 d.p.)Thus, the shortest distance is 7.1587 m.
Diagram 10 shows the position of three campsites A, B and C at a part of a riverbank drawn on a Cartesian plane, such that A and B lie on the same straight riverbank.
 Diagram 10
Diagram 10Sam wants to cross the river from campsite C to the opposite riverbank where the campsites A and B are located.
Find the shortest distance, in m, that he can take to cross the river. Give your answer correct to four decimal places.
Solution:
Let the shortest distance from campsite Cto opposite riverbank is CD.Area of △ABC=12|−2 7 4 3 5 −3 −2 3|=12|(−2)(5)+(7)(−3)+(4)(3)−(3)(7)−(5)(4)−(−3)(−2)|=12|−66|=33 units2Distance of AB=√(−2−7)2+(3−5)2=√85 mArea of △ABC=3312(AB)(CD)=3312(√85)(CD)=33CD=33(2)√85CD=7.1587 (4 d.p.)Thus, the shortest distance is 7.1587 m.
 Diagram
Diagram