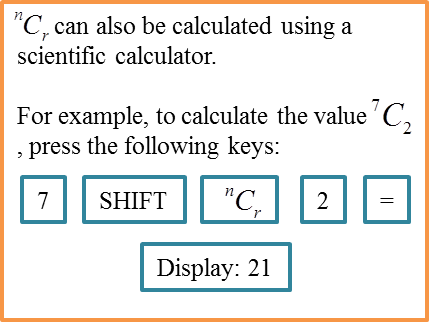
Question 1:
A group of 4 men and 3 ladies are to be seated in a row for a photographing session. If the men and ladies want to be seated alternately (man-lady-man-lady...), calculate the number of different arrangements.
Solution:
The arrangements of 4 men and 3 ladies to be seated alternately are as follow:
M L M L M L M
The number of ways to arrange the seat for 4 men = 4!
The number of ways to arrange the seat for 3 ladies = 3!
Total number of different arrangements for men and ladies = 4! × 3! = 144
Question 2:
Ahmad has 6 durians, 5 watermelons and 2 papayas. If he wants to arrange these fruits in a row and the fruits of the same kind have to be grouped together, calculate the number of different arrangements. The sizes of the fruits are different.
Solution:
The number of ways to arrange 3 groups of fruits that are same kind = 3!
DDDDDD WWWWW PP
The number of ways to arrange 6 durians = 6!
The number of ways to arrange 5 watermelons = 5!
The number of ways to arrange 2 papayas = 2!
Therefore, the number of ways to arrange the fruits with same kind of fruits was grouped together
= 3! × 6! × 5! × 2!
= 1036800
Ahmad has 6 durians, 5 watermelons and 2 papayas. If he wants to arrange these fruits in a row and the fruits of the same kind have to be grouped together, calculate the number of different arrangements. The sizes of the fruits are different.
Solution:
The number of ways to arrange 3 groups of fruits that are same kind = 3!
DDDDDD WWWWW PP
The number of ways to arrange 6 durians = 6!
The number of ways to arrange 5 watermelons = 5!
The number of ways to arrange 2 papayas = 2!
Therefore, the number of ways to arrange the fruits with same kind of fruits was grouped together
= 3! × 6! × 5! × 2!
= 1036800
Question 3:
Calculate the number of arrangements, without repetitions, of the letters from the word `SOMETHING' with the condition that they must begin with a vowel.
Solution:
Arrangement of letters begin with vowel = O, M and I= 3P1Arrangement for the rest of the letters= 7!∴Number of arrangements = 3P1×7!=15120
Calculate the number of arrangements, without repetitions, of the letters from the word `SOMETHING' with the condition that they must begin with a vowel.
Solution:
Arrangement of letters begin with vowel = O, M and I= 3P1Arrangement for the rest of the letters= 7!∴Number of arrangements = 3P1×7!=15120