If δx is very small, δyδx will be a good approximation of dydx, ,
[adinserter block="3"]
The small change in y is denoted by δy while the small change in the second quantity that can be seen in the question is the x and is denoted by δx.
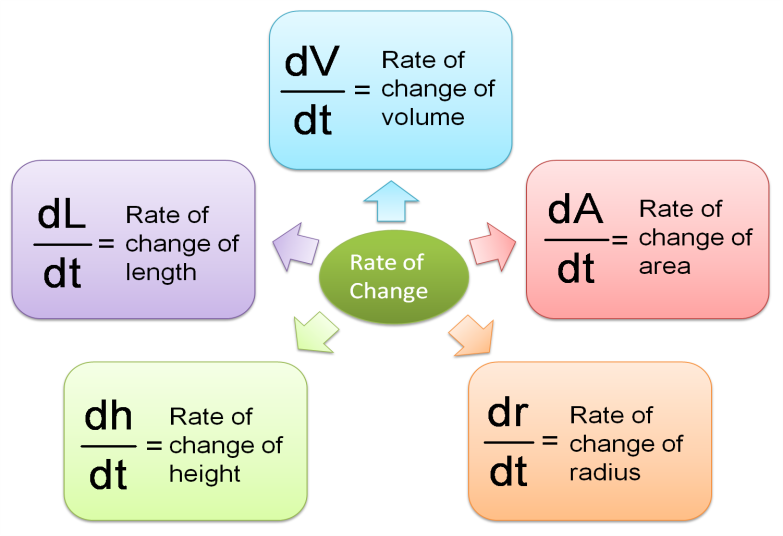
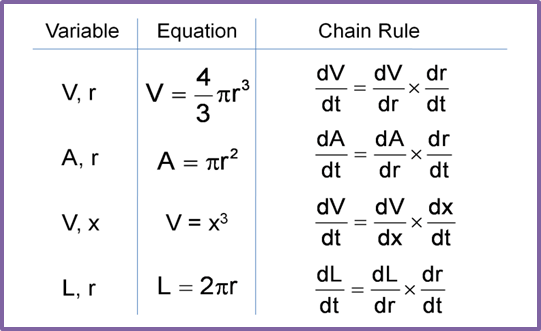
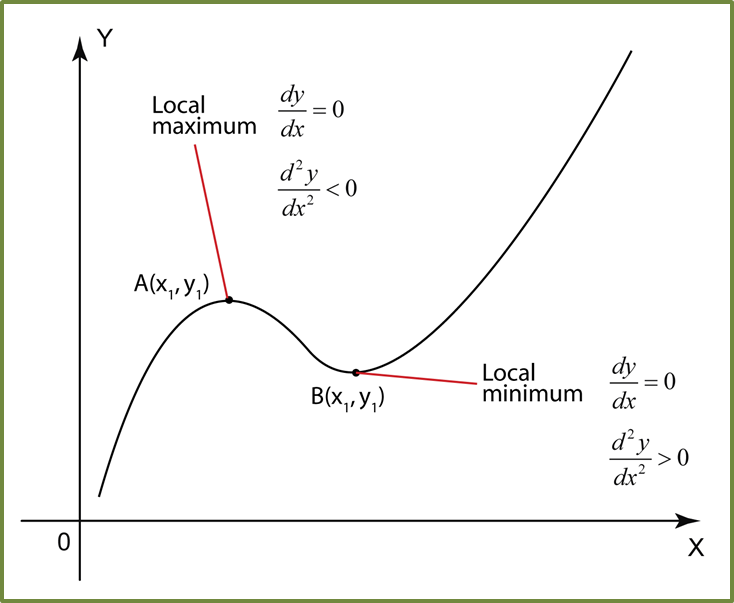
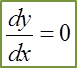


Find the Derivatives of a Quotient using Quotient Rule
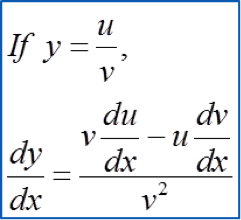
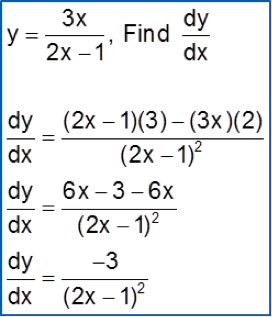
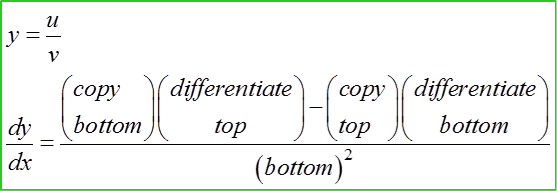
Given thaty=x22x+1,finddydx
y=x22x+1dydx=(2x+1)(2x)−x2(2)(2x+1)2=4x2+2x−2x2(2x+1)2=2x2+2x(2x+1)2
Given thaty=4x3(5x+1)3,finddydx
y=4x3(5x+1)3dydx=(5x+1)3(12x2)−4x3.3(5x+1)2.5[(5x+1)3]2=(5x+1)3(12x2)−60x3(5x+1)2(5x+1)6=(12x2)(5x+1)2[(5x+1)−5x](5x+1)6=(12x2)(5x+1)2(1)(5x+1)6=12x2(5x+1)4
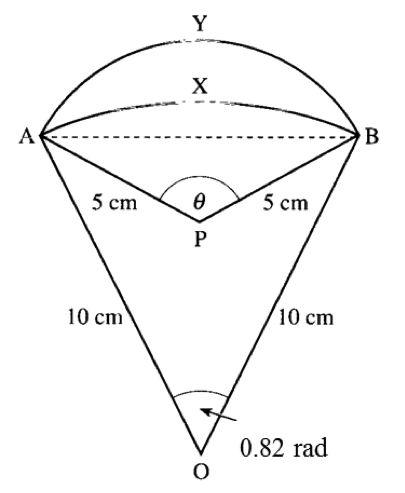
In the diagram above, AXB is an arc of a circle centre O and radius 10 cm with ∠AOB = 0.82 radian. AYB is an arc of a circle centre P and radius 5 cm with ∠APB = θ. Calculate:
(a)
12AB=sin0.41×10→(Change the calculator to Rad mode)12AB=3.99∴The length of chordAB=3.99×2=7.98cm.
(b)
Let12θ=α,θ=2αsinα=3.995α=0.924rad∴θ=0.924×2=1.848radian.
(c)
Using s = rθ
Arcs AXB = 10 × 0.82 = 8.2 cm
Arcs AYB = 5 × 1.848 = 9.24 cm
Difference in length between the arcs AYB and AXB
= 9.24 – 8.2
= 1.04 cm
 It is given that OP = 17 cm and PQ = 8.8 cm.
It is given that OP = 17 cm and PQ = 8.8 cm.