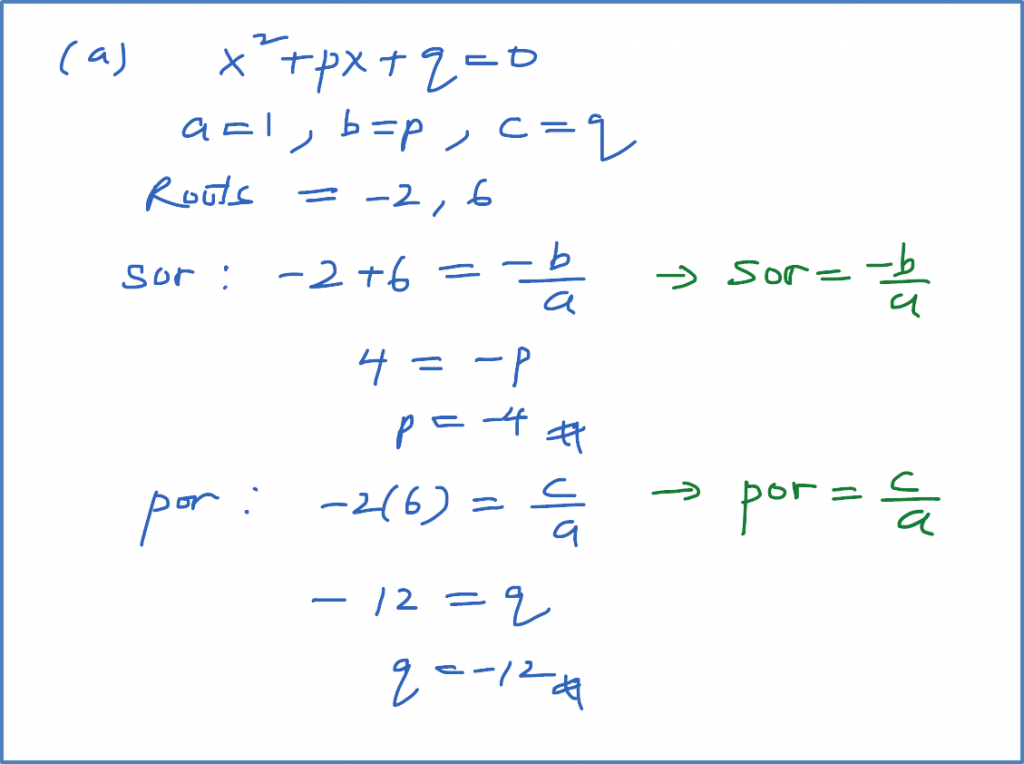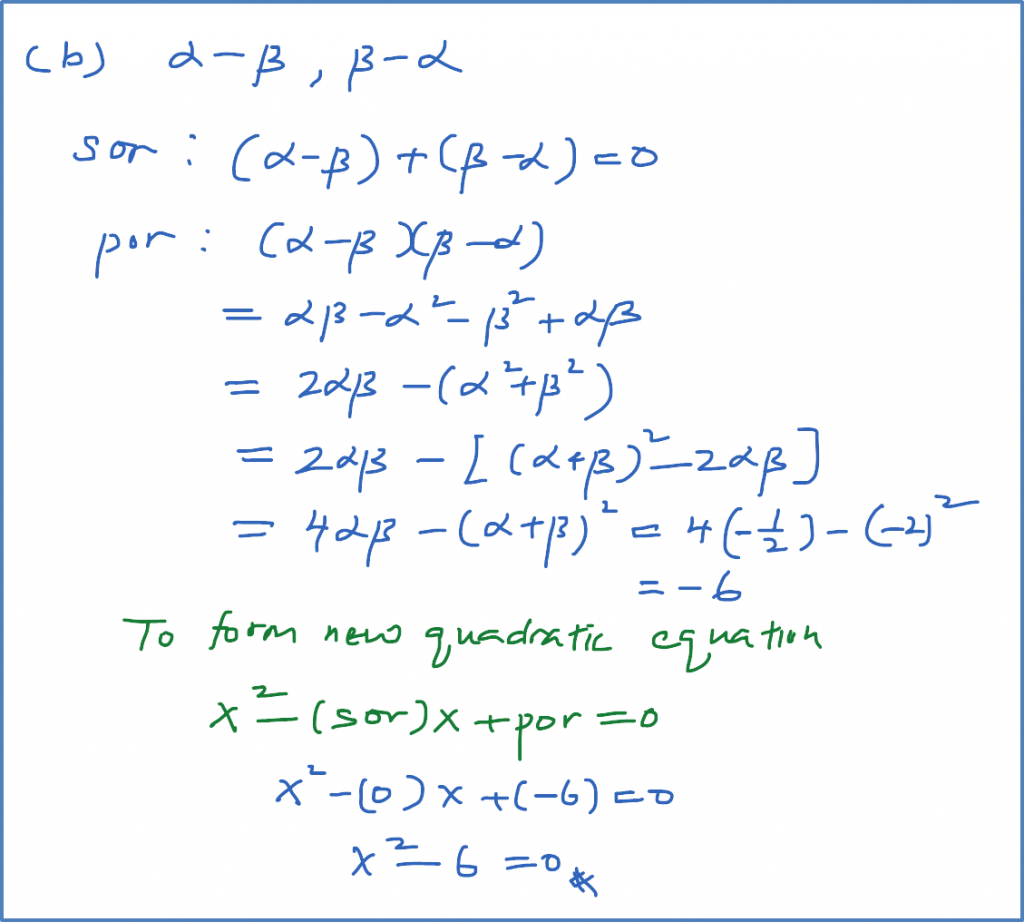Question 11:
Solve the following quadratic equation:
5x+3x21−2x=6
Solution:
5x+3x21−2x=65x+3x2=6−12x3x2+5x+12x−6=03x2+17x−6=0(3x−1)(x+6)=03x−1=0 or x+6=0 3x=1 x=−6 x=13 x=−6
Solve the following quadratic equation:
5x+3x21−2x=6
Solution:
5x+3x21−2x=65x+3x2=6−12x3x2+5x+12x−6=03x2+17x−6=0(3x−1)(x+6)=03x−1=0 or x+6=0 3x=1 x=−6 x=13 x=−6
Question 12:
Diagram above shows a rectangle ABCD.
(a) Express the area of ABCD in terms of n.
(b) Given the area of ABCD is 60 cm2, find the length of AB.
Solution:
(a)
Area of ABCD
= (n + 7) × n
= (n2+ 7n) cm2
(b)
Given the area of ABCD = 60
n2+ 7n = 60
n2+ 7n – 60 = 0
(n – 5) (n + 12) = 0
n = 5 or n = – 12 (not accepted)
When n = 5,
Length of AB = 5 + 7 = 12 cm
Question 13 (4 marks):
Solve the following quadratic equation:
−23x−5=x3x−1
Solution:
−23x−5=x3x−1−2(3x−1)=x(3x−5)−6x+2=3x2−5x3x2−5x+6x−2=03x2+x−2=0(3x−2)(x+1)=03x−2=0 or x+1=0x=23 or x=−1
Solve the following quadratic equation:
−23x−5=x3x−1
Solution:
−23x−5=x3x−1−2(3x−1)=x(3x−5)−6x+2=3x2−5x3x2−5x+6x−2=03x2+x−2=0(3x−2)(x+1)=03x−2=0 or x+1=0x=23 or x=−1