Question 11 (10 marks):
Solution by scale drawing is not accepted.
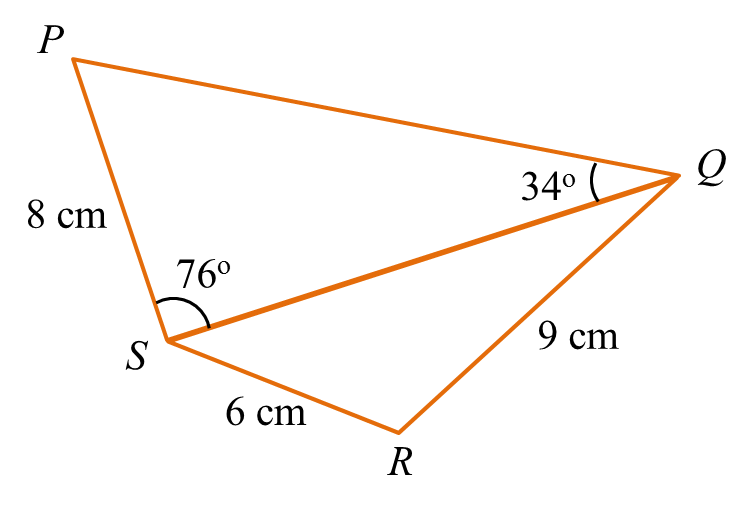
Diagram shows a quadrilateral PQRS on a horizontal plane.
 VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.
VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.
Find
(a) ∠QSR,
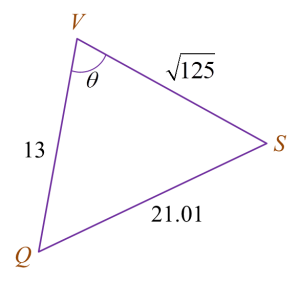
(b) the length, in m, of QS,
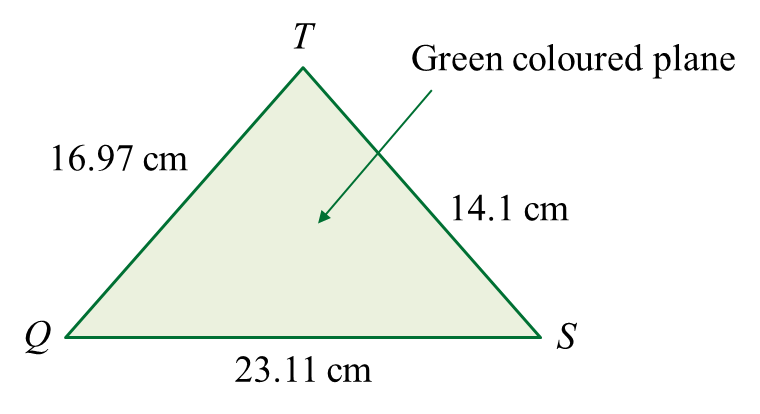
(c) the area, in m2, of inclined plane QVS.
Solution:
(a)
sin∠QSR20.5=sin64o22sin∠QSR=sin64o22×20.5sin∠QSR=0.8375∠QSR=56o52'
(b)
(c)
Solution by scale drawing is not accepted.
Diagram shows a quadrilateral PQRS on a horizontal plane.
 VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.
VQSP is a pyramid such that PQ = 12 m and V is 5 m vertically above P.Find
(a) ∠QSR,
(b) the length, in m, of QS,
(c) the area, in m2, of inclined plane QVS.
Solution:
(a)
sin∠QSR20.5=sin64o22sin∠QSR=sin64o22×20.5sin∠QSR=0.8375∠QSR=56o52'
(b)
(c)

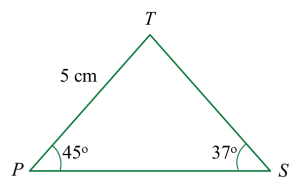
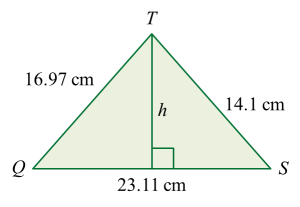

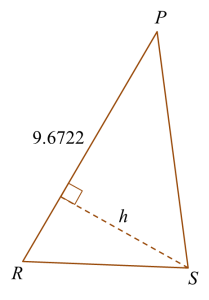
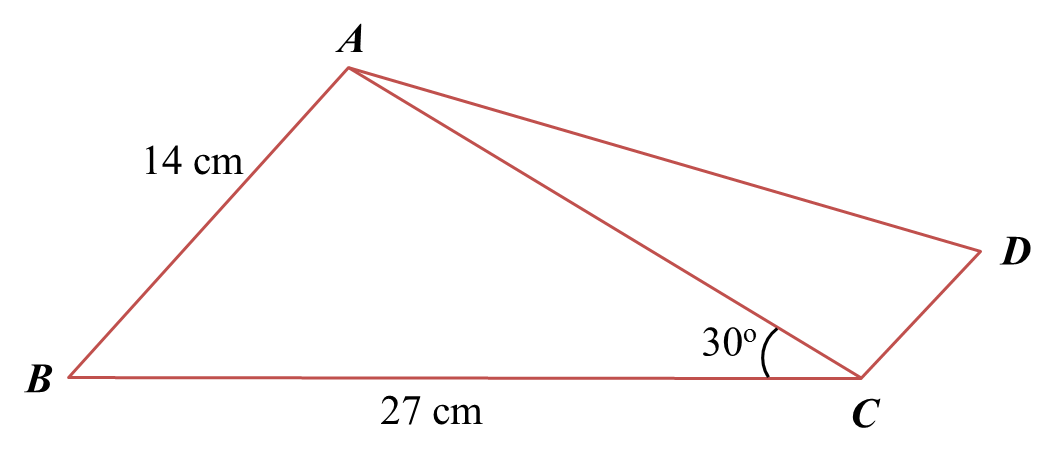
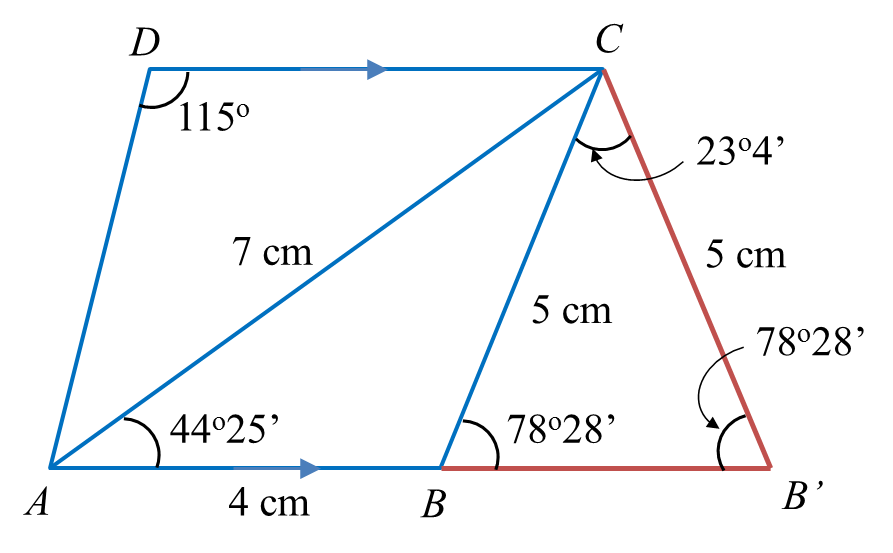
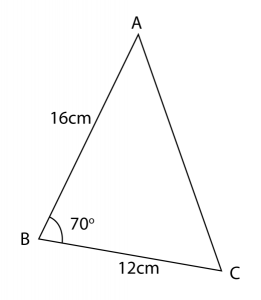
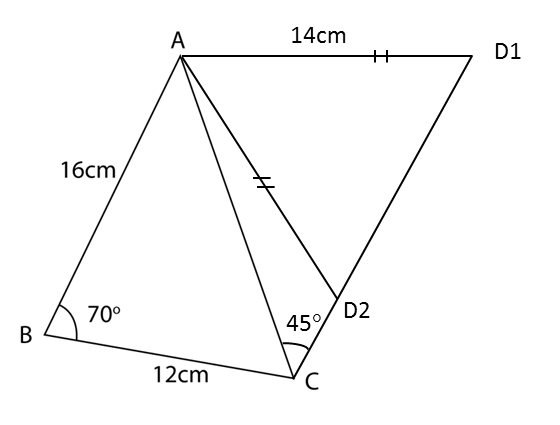
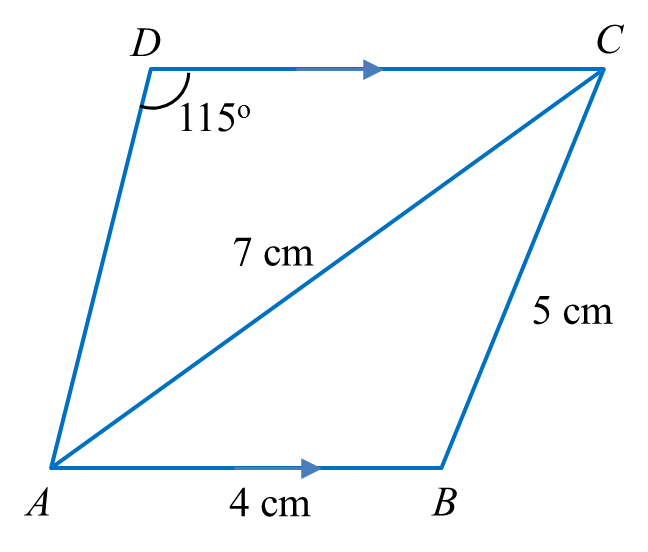 (a) Calculate
(a) Calculate