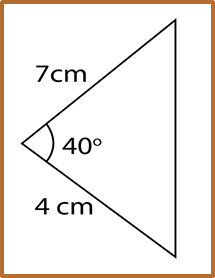
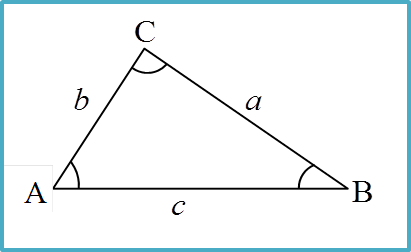
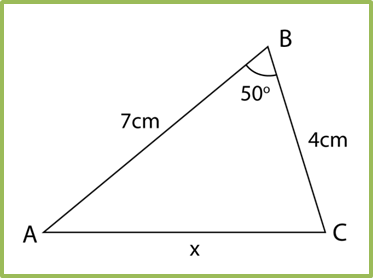
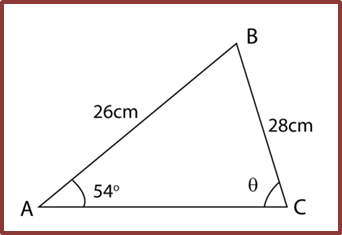
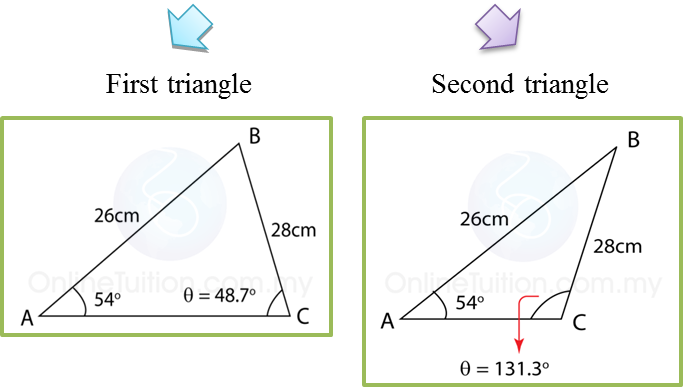
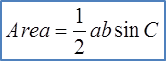Example:
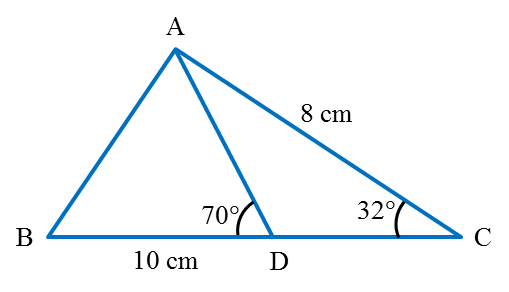
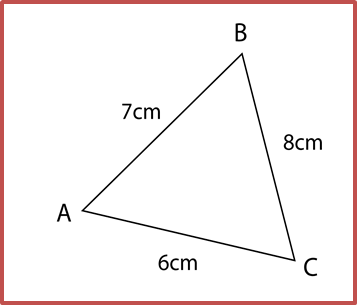
Diagram above shows a triangle ABC, where AC = 8 cm and ∠C = 32o. Point D lies on straight line BC where BD = 10 cm and ∠ADB = 70o . Calculate
(a) the length, in cm, of CD,
(b) the area, in cm2 of ∆ ADC,
(c) the area, in cm2 of ∆ ABC,
(d) the length, in cm, of AB.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)

Diagram above shows a triangle ABC, where AC = 8 cm and ∠C = 32o. Point D lies on straight line BC where BD = 10 cm and ∠ADB = 70o . Calculate
(a) the length, in cm, of CD,
(b) the area, in cm2 of ∆ ADC,
(c) the area, in cm2 of ∆ ABC,
(d) the length, in cm, of AB.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)