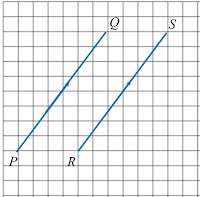
Example 1:
(a) The resultant vector of the addition of the two parallel vectors above
(b) The magnitude of the resultant vector.
Solution:
(a)
Resultant vector
= addition of the two vectors
=→PQ+→RS
(b)
Magnitude of the resultant vector
=|→PQ|+|→RS|=|√62+82|+|√62+82|=10+10=20unitsExample 2:
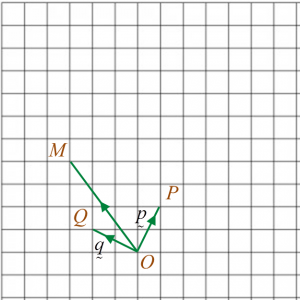
(a)→OB(b)→MB(c)→OM
Solution:
(a)
→OB=→OA+→AB←Triangle Law of addition=→OA+→OC←→AB=→OC=a˜+c˜
(b)
→MB=12→CB←M is the midpoint of CB =12→OA =12a˜
(c)
→OM=→OC+→CM←Triangle Law of addition=→OC+→MB←→CM=→MB=c˜+12a˜
(b)
→MB=12→CB←M is the midpoint of CB =12→OA =12a˜
(c)
→OM=→OC+→CM←Triangle Law of addition=→OC+→MB←→CM=→MB=c˜+12a˜

 Diagram
Diagram Diagram
Diagram Diagram
Diagram