Theory of Cell
- The cell is the basic unit or building block for all living organisms.
- All organisms are made up of one or more cells .
- Cells are the fundamental and structural unit of life.
A cell is made up of a plasma membrane which contains protoplasm.
Protoplasm is made up of cytoplasm and a nucleus.
A cell consist of the non-organelle structure the organelle structure.
Non-organelle/Organelle Structures of Cell
- The non organelle structure of a cell include
- Plasma membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Cell wall (plant cell only)
- Whereas the organelle structure of a cell include
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic Recticulum
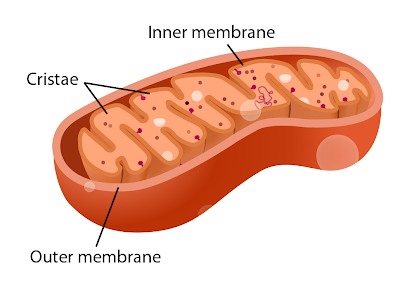
- Mitochondrion
- Ribosom
- Golgi apparatus
- Vacuole
- Chloroplast (plant cell only)
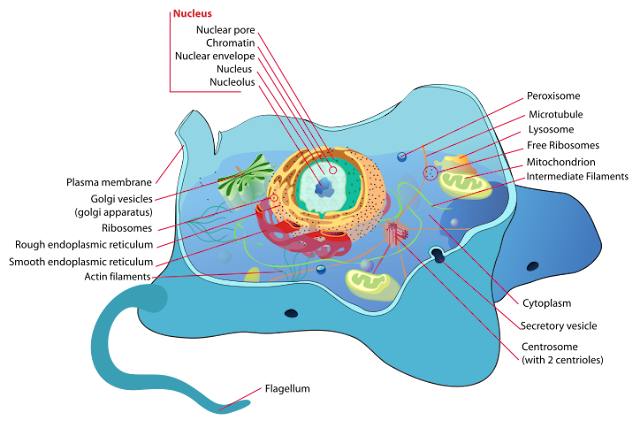
Structure of an Animal Cell
- Each animal cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane.
- Within the plasma membrane is the protoplasm which consists of the cytoplasm and a nucleus.
- Animal cells do not have regular shapes.
 |
| (This file is shared under GNU Share Document Licence from Wikipedia) |
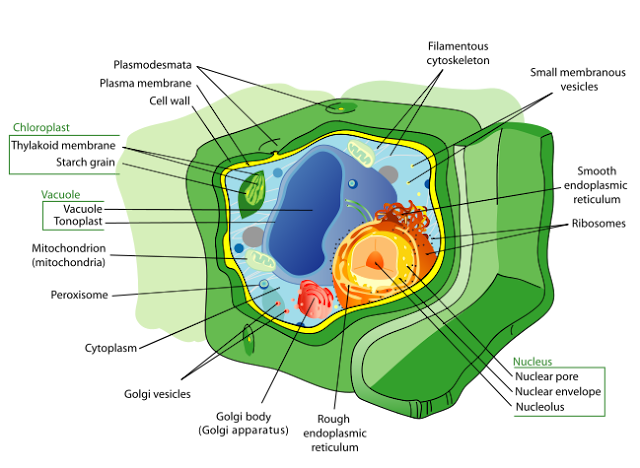
Structure of a Plant Cell
- Each plant cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane which is protected by a cell wall.
- Again, within the plasma membrane has a nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Unlike animal cell, most plant cells have chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll.
- Also, a mature plant cell may have a large vacuole which contains cell sap.
- Plant cells have a fixed shape because they have cell walls.
 |
| (Onion Cell) |