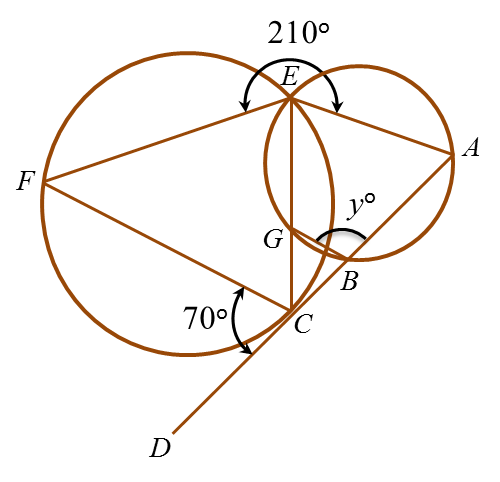
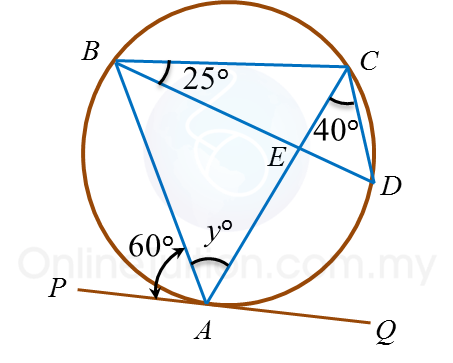
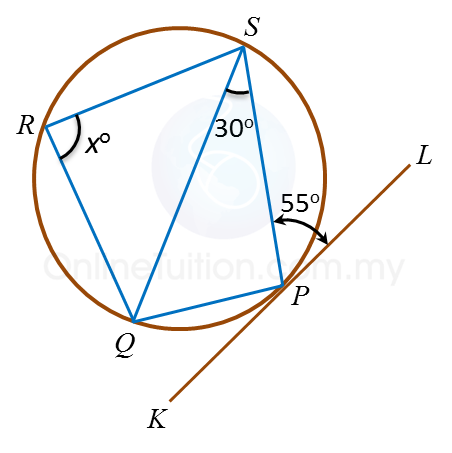
Example 1:
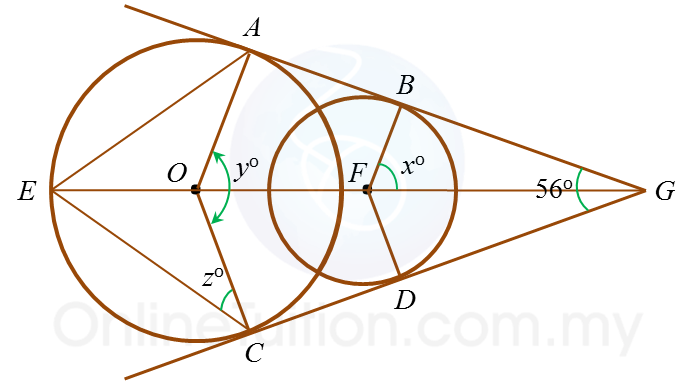
In the diagram, ABG and CDG are two common tangents to the circle with centres O and F respectively. Find the values of
(a) x, (b) y, (c) z.
Solution:
(a)
In ∆ BFG,
angle BFG = ½ × 56o = 28o
angle FBG = 90o ← (tangent is 90o to radius)
xo + 28o + 90o = 180o
xo = 180o – 118o
xo = 62o
x = 62
(b)
angle AOF = xo = 62o ← (AO// BF)
yo = 2 × 62o
yo = 124o
y = 124
(c)
Exterior angle of AOC = 360o – 124o = 236o
Angle EOC = ½ × 236o = 118o
zo = (180o – 118o) × ½ ← (∆ EOC is isosceles triangle, angle OEC = angle OCE)
zo = 31o
z = 31