- The resistance R of a material is defined as the ratio V : I, where V is the potential difference across the material and I is the current flowing in it.

- The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (W). One ohm is the resistance of a material through which a current of one ampere flows when a potential difference of one volt is maintained.
Finding Resistance from the Potential Difference - Current Graph
In the graph potential difference against current, the gradient of the graph is equal to the resistance of the resistor.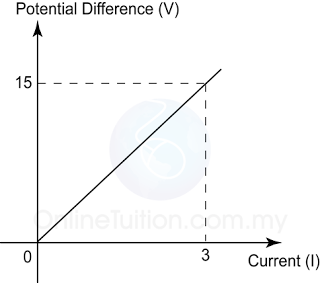
Figure above shows the graph of potential difference across a wire against its current. Find the resistance of the wire.
Answer:
Resistance
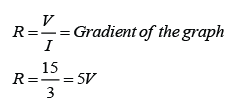
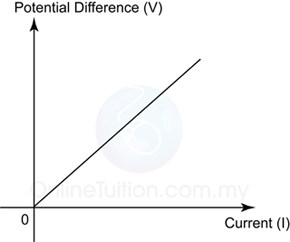
Ohmic Conductor
- Conductors that obey Ohm’s law are said to be ohmic conductor.
- Examples of Ohmic conductor: Metal, Copper sulphate solution with copper electrodes
Non-Ohmic Conductor
- Conductors which do not obey Ohm’s law are called non-ohmic conductor.
- Example: Semiconductor Diode, Vacuum tube diode
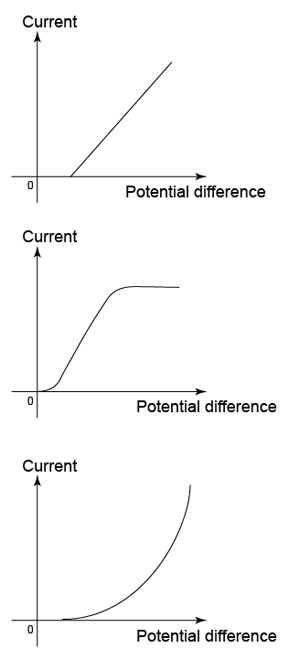 |
| (Examples of characteristic of non-Ohmic conductor) |
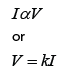

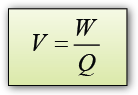
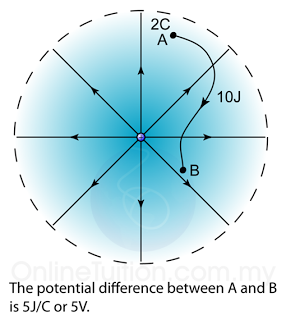
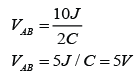
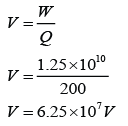
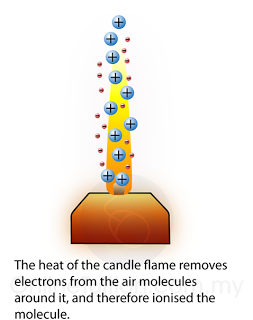
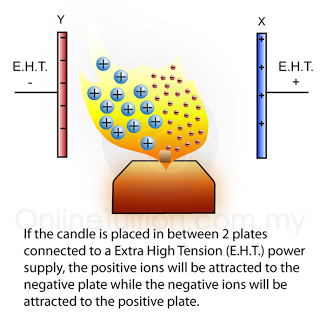
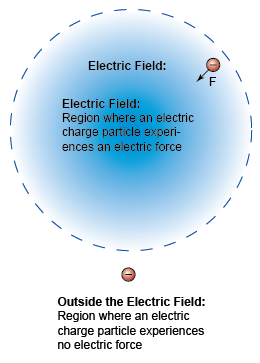
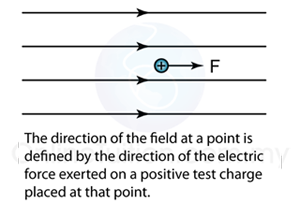
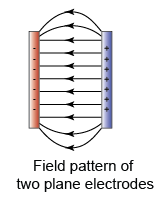
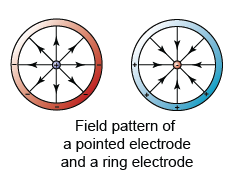
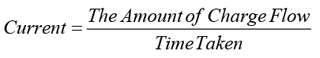
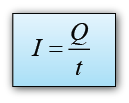

.png)