[adinserter block="3"]
Question 6:
(a) Diagram 6.1 shows a gaseous exchange in the alveolus.
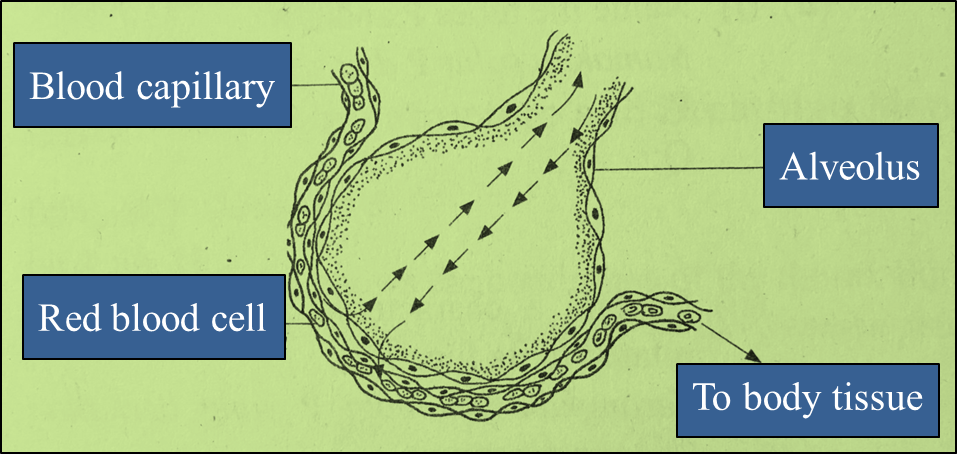 Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.1
Explain how oxygen is transported to the body tissues for cellular respiration. [4 marks]
(b)

Based on the statement above, suggest and explain how to keep our lungs healthy. [6 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
(c) Diagram 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 show the respiratory organ from two different organisms.
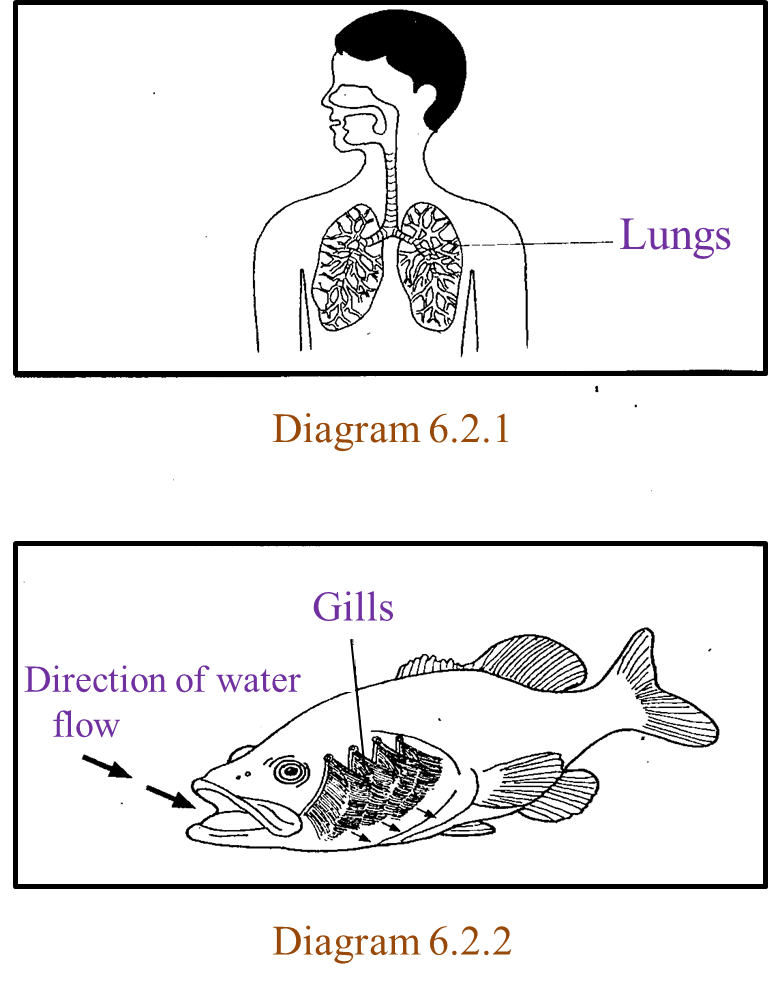
Explain similarities and differences in structures of the respiratory organ between the two organisms. [10 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)
- Oxygen gas in the alveoli is at higher partial pressure / higher concentration than in blood.
- Oxygen molecules diffuse across epithelium of alveoli and blood capillaries into blood.
- Oxygen binds with haemoglobin in the red blood cells / erythrocytes to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- The oxygenated blood is then transported from the lungs to cells of body tissues.
- In the tissues, oxyhaemoglobin dissociates into oxygen and haemoglobin.
- Oxygen diffuses down a concentration gradient across the epithelia of blood capillaries into the cells of body tissues.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)
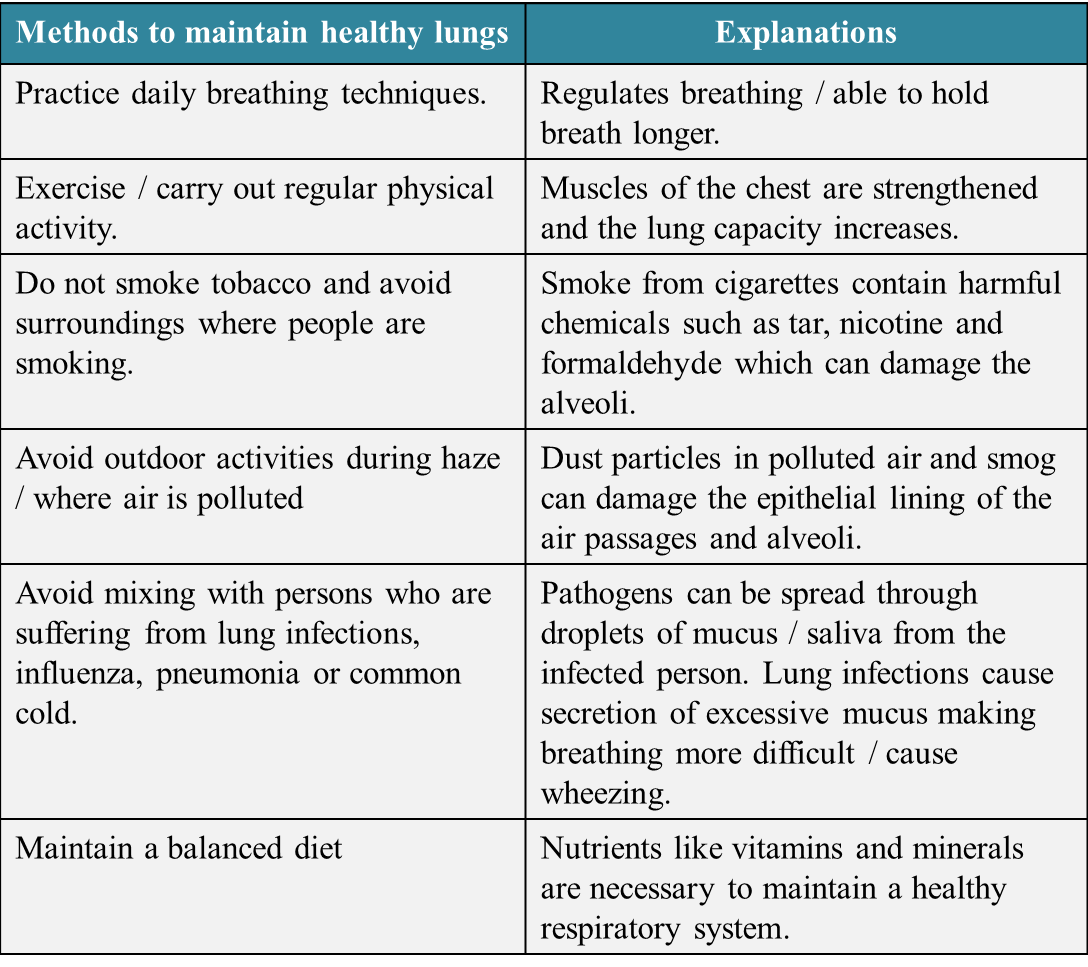
[adinserter block="3"]
(c)
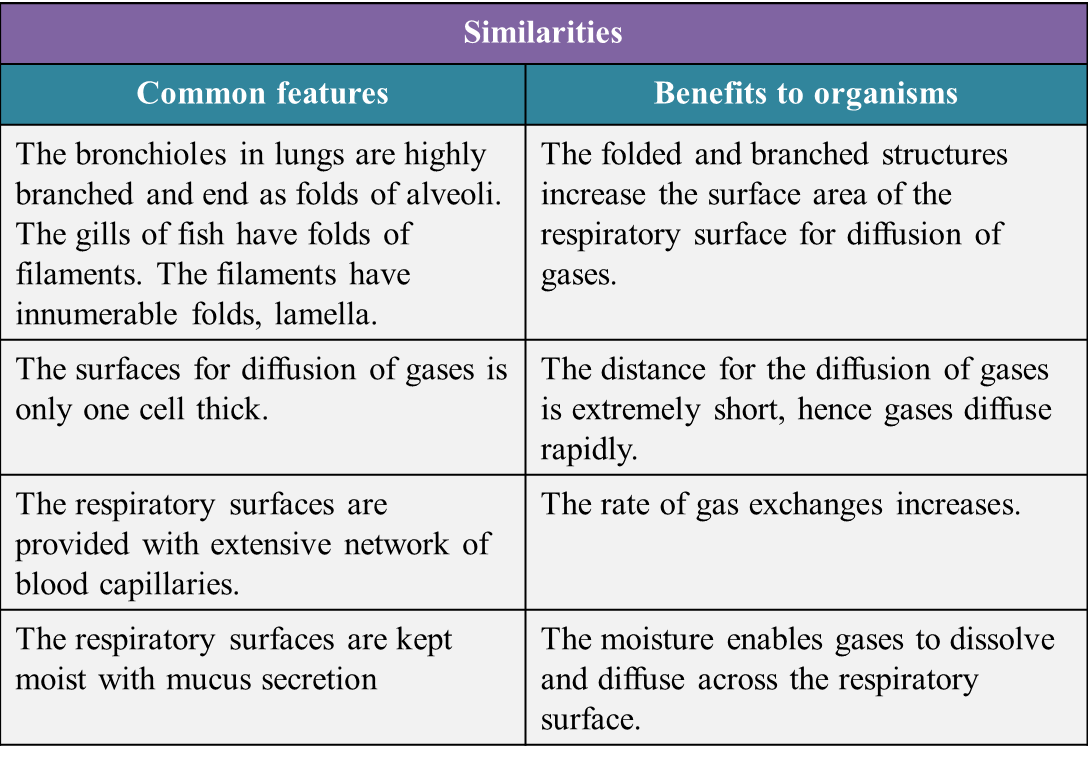
[adinserter block="3"]
(a) Diagram 6.1 shows a gaseous exchange in the alveolus.
 Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.1Explain how oxygen is transported to the body tissues for cellular respiration. [4 marks]
(b)

Based on the statement above, suggest and explain how to keep our lungs healthy. [6 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
(c) Diagram 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 show the respiratory organ from two different organisms.

Explain similarities and differences in structures of the respiratory organ between the two organisms. [10 marks]
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)
- Oxygen gas in the alveoli is at higher partial pressure / higher concentration than in blood.
- Oxygen molecules diffuse across epithelium of alveoli and blood capillaries into blood.
- Oxygen binds with haemoglobin in the red blood cells / erythrocytes to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- The oxygenated blood is then transported from the lungs to cells of body tissues.
- In the tissues, oxyhaemoglobin dissociates into oxygen and haemoglobin.
- Oxygen diffuses down a concentration gradient across the epithelia of blood capillaries into the cells of body tissues.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)

[adinserter block="3"]
(c)

[adinserter block="3"]

 Diagram 5
Diagram 5
 Diagram 6
Diagram 6

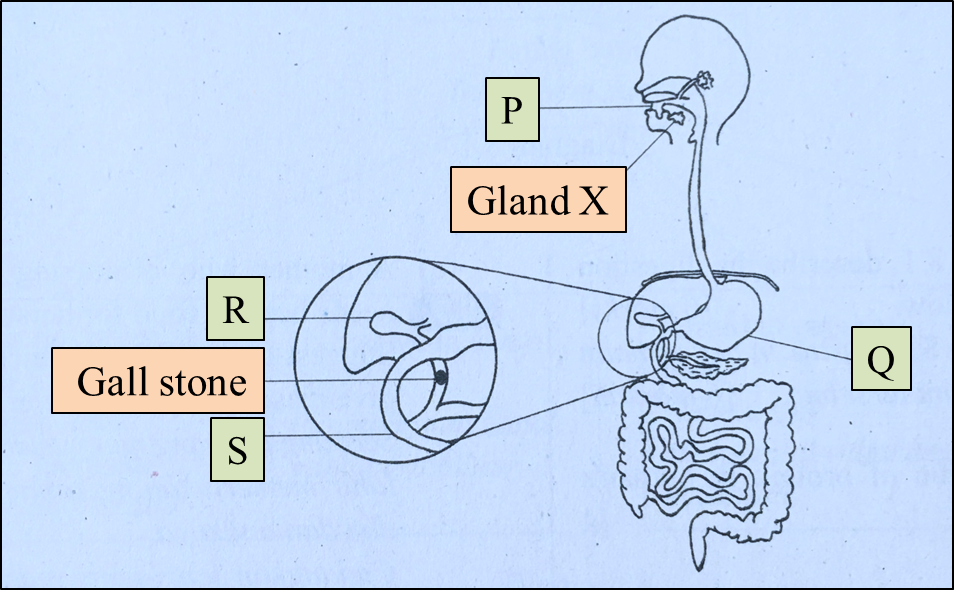 Diagram 3
Diagram 3 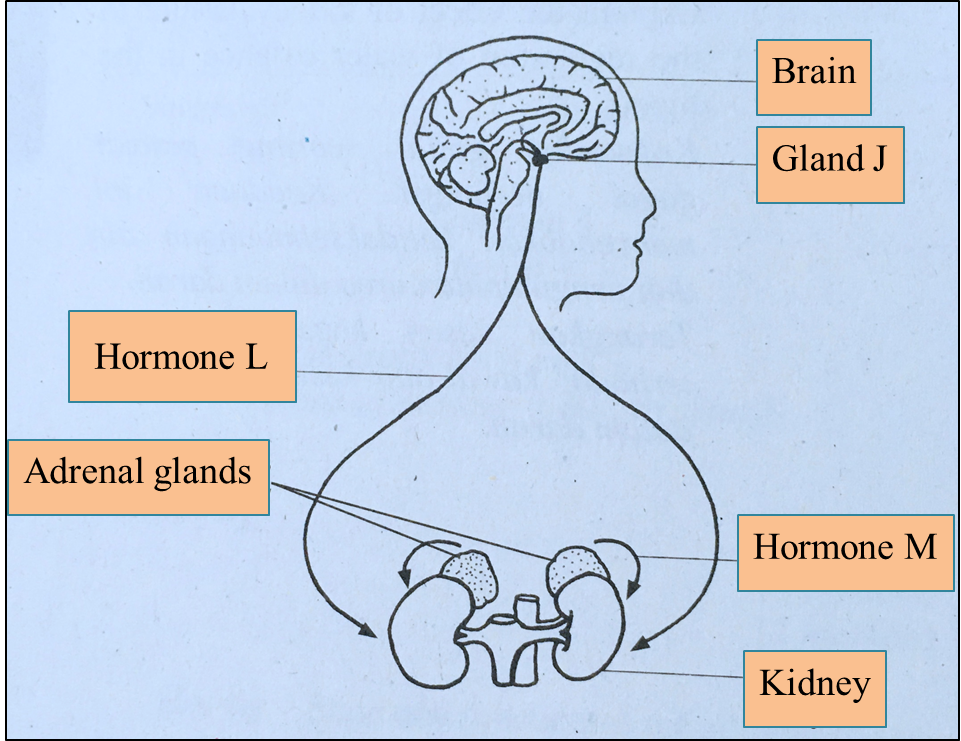 Diagram 4.1
Diagram 4.1
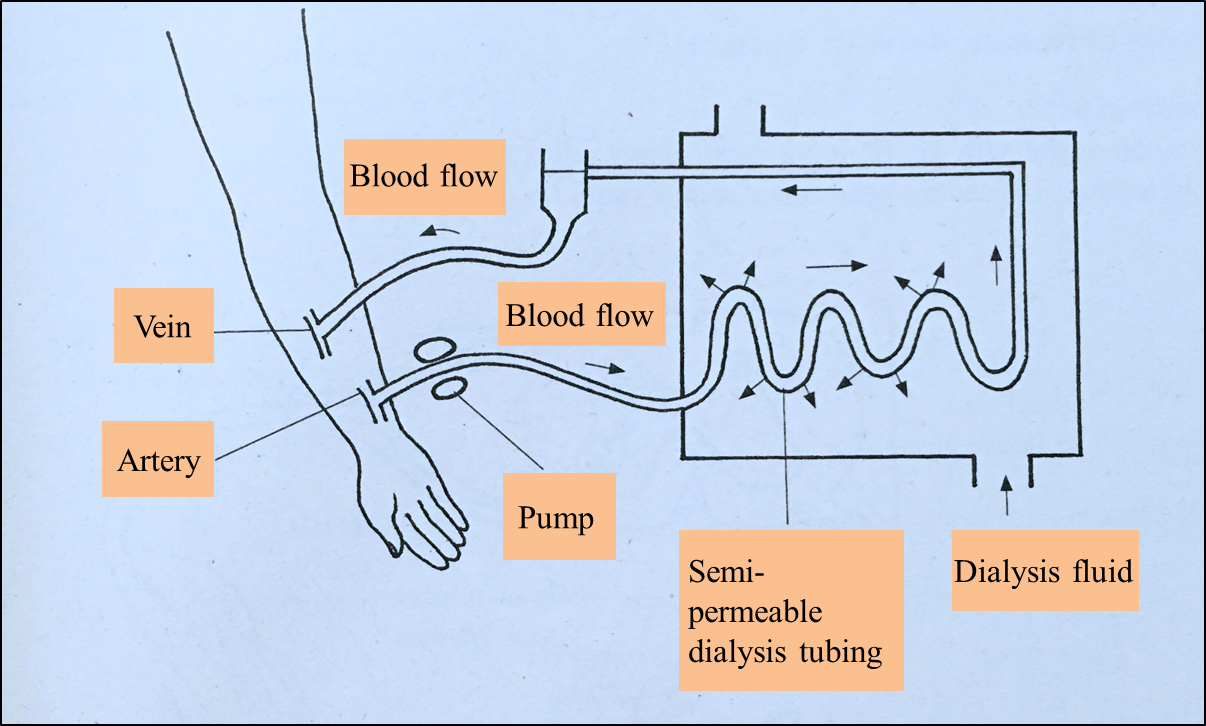 Diagram 4.2
Diagram 4.2
 Table 1
Table 1



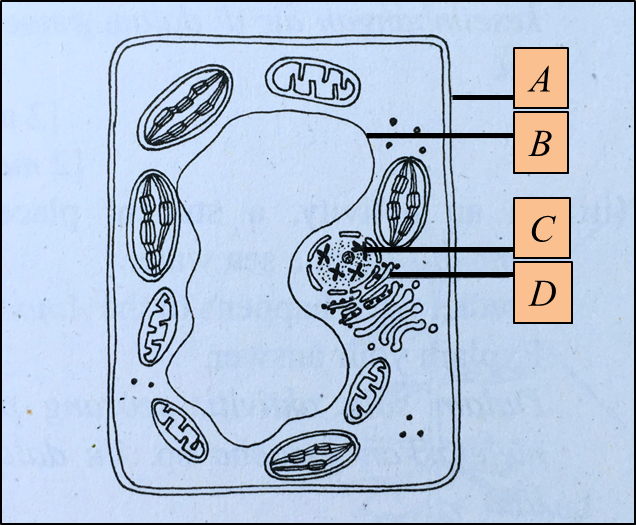 Diagram 1.1
Diagram 1.1 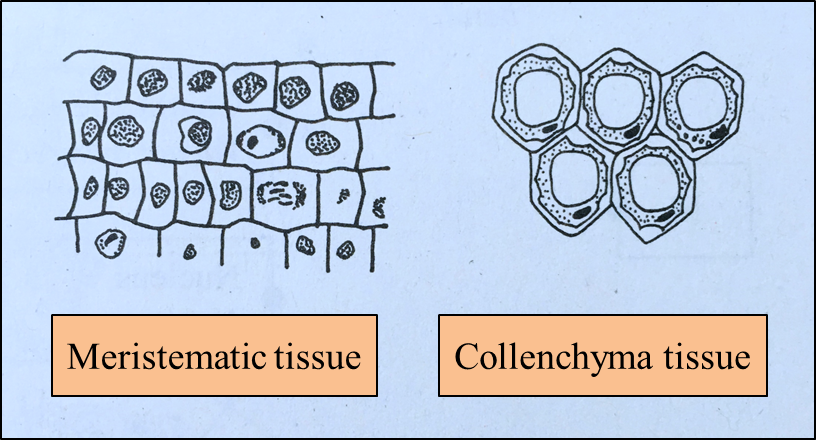 Diagram 1.2
Diagram 1.2 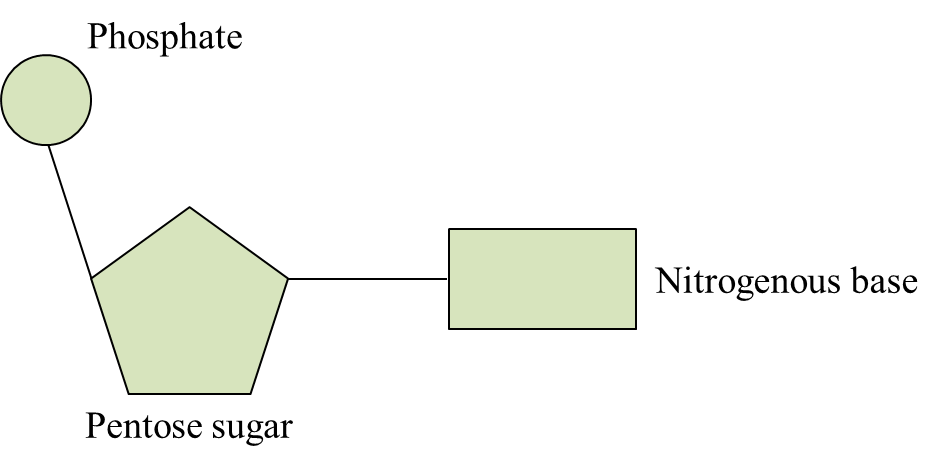
 Diagram 2.1
Diagram 2.1 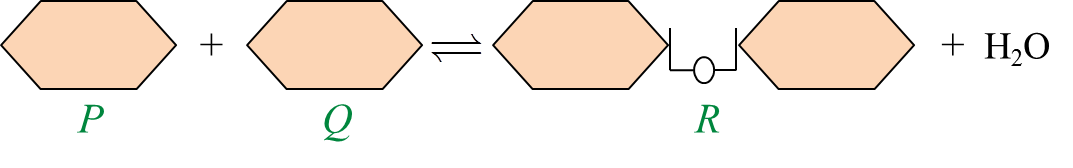 Diagram 2.2
Diagram 2.2


 Diagram 9
Diagram 9

 Diagram 7.1
Diagram 7.1 Diagram 7.2
Diagram 7.2
 Diagram 8.1
Diagram 8.1 Diagram 8.2
Diagram 8.2

 Diagram 5.1
Diagram 5.1

 Diagram 5.2
Diagram 5.2 Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.1 Diagram 6.2
Diagram 6.2 Diagram 3
Diagram 3