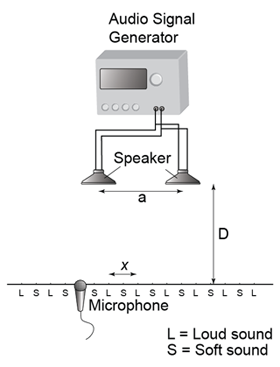
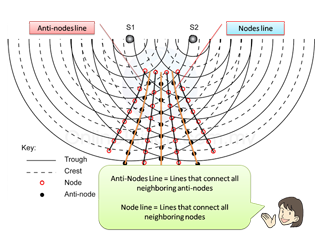
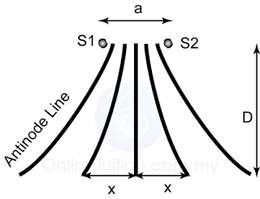
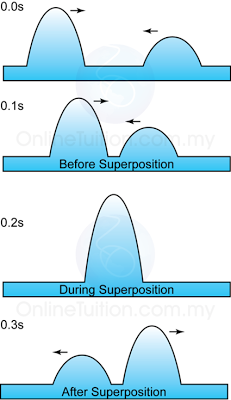
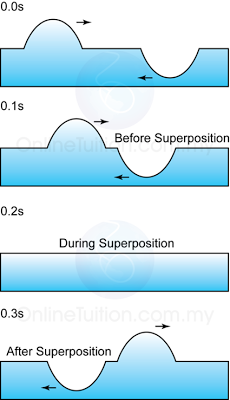
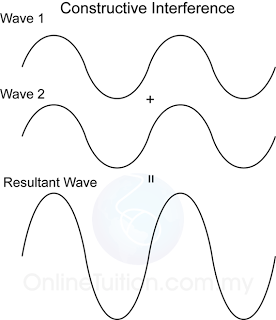
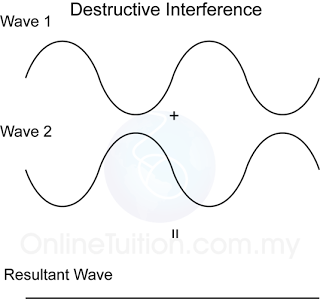
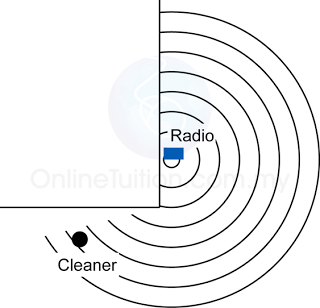
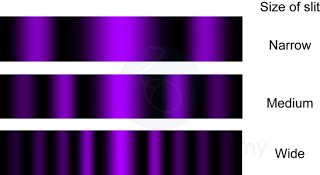
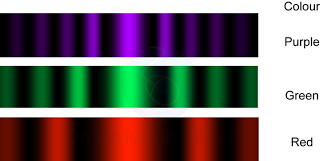
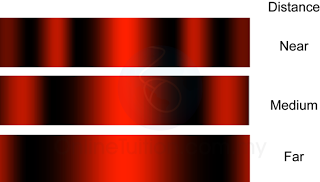
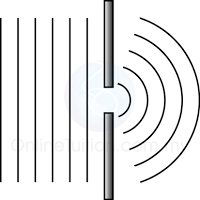
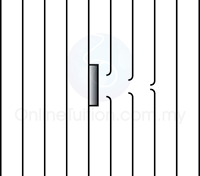
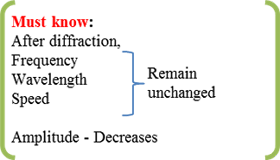
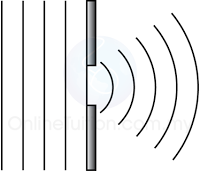
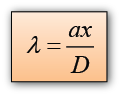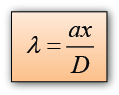Characteristic of Sound Wave
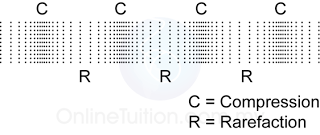
- Sound wave is a series of compression and rarefaction of layers of air molecules repeatedly through space.
- The forward and backward vibration of the air molecules in the direction of motion of a sound wave shows that sound is a longitudinal wave.
Propagation of Sound Wave
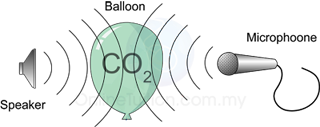
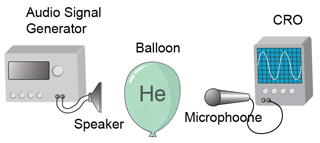
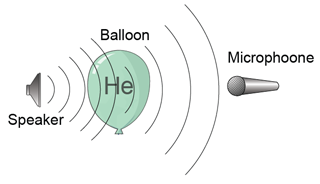
- Sound wave is a mechanical wave that requires a medium for its propagation. Therefore sound wave cannot propagate in vacuum.
- The medium for propagation can be solid, liquid or gas.
- Sound waves propagate fastest in solid and slowest in gas.
Type of Sound Wave
- Human ear is capable of hearing sound with frequency in the range of 20Hz – 20,000Hz, and the sound wave with frequency in this range is called an audio/Sonic wave.
- Sound wave with frequency lower than 20Hz is called an Infrasonic Wave.
- Sound wave with frequency higher than 20,000Hz is called an Ultrasonic wave.
| Infrasonic | Audio/Sonic | Ultrasonic |
| <20Hz | 20Hz – 20000Hz | >20 kHz |
Speed of Sound Wave
- Speed of sound wave in solids is greater than in liquids, which is greater than in gases.
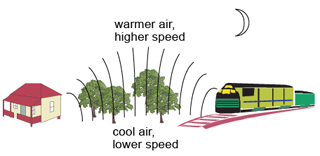
- Speed of sound in air is not affected by pressure, but is affected by the temperature.
- As temperature increases, speed of sound in air (and other gases) is also increases.
- Sound usually travels more slowly with greater altitude, due to reduced temperature.
- Speed of sound can be calculated by the equation